To be - the basis of English grammar. If you misunderstood or understudied this material, then your entire study of the English language will most likely be unsuccessful. Therefore, if you feel that there is a gap somewhere in this material, then it is better to stay longer on this page.
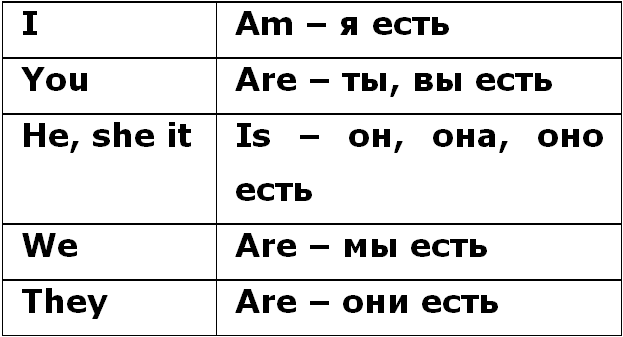
Drawing. Conjugation of the verb to be (am, is, are) in the present tense
This verb is translated as “to be, to exist, to be available, to appear.” In short, everything that is translated in Russian as “eat” (not in the sense of “eating food”) is translated into English by this verb.
The whole problem and the difficulty is that in Russian this verb is omitted:
- This is an apple = This is an apple
- She is a doctor = She is a doctor
Agree, we don’t use the second options. But the translation of such sentences must correspond precisely to the second option.
Difficulty #2 is that to be changes its form depending on which pronoun it comes after. Taking into account all of the above, the forms of this verb look like this.
Table.
It's easy to remember: plural to be always takes shape are . We already know about the pronoun you that in both translations - “you” and “you” - it is still placed in the plural. All that remains to be remembered is I am And He/ She/ It is .
Naturally, the same rules apply to nouns that can be replaced by these pronouns.
- He is in the office.
- Lara (=She) is beautiful.
- These apples (=they) are not fresh.
Negative and interrogative forms of to be
To get negative, put after the form to be particle not .
- His friend is not (=isn’t) young.
- We are not (=aren’t students).
As for the questions, the form to be is placed at the very beginning of the question - before the subject. That is,
To turn a statement into a question, you simply need to swap the subject and predicate.
- They are in the cinema.
- They aren't in the cinema.
- Are they in the cinema?
- Where are they?
It is with this verb that you need to start studying English grammar. Verbs in English language do not vary by person, but the verb to be is an exception. Using this verb, we will learn to compose simple sentences that do not contain a verb in Russian, for example, “I am a student,” “he is at home,” “this is interesting,” etc. In English it is unacceptable to form without a verb that performs the action, and to be serves as a linking verb. For example, to say “I am a student,” we must insert the desired form of the linking verb to be and, as a result, the sentence will take on the meaning “I am a student” - “I (am) a student.”
Forms of the verb to be in the present tense
In the present tense, the verb to be has three forms: AM, IS, ARE:
- Remember: to be and AM, IS, ARE are not 4 different ones, but forms the same verb:
Google shortcode

(We hope our dragon will help you remember this)
Let's look at how the verb to be changes in the present tense
Affirmative form
- We are friends - we are friends
- They are busy - they are busy
- The book is thick - the book is thick
- It is a cat
- She is clever - she is smart
Negative form

To form a negative conjugation form of a given verb, you need to put a negative particle “not” after one of required forms verb (am, is or are). Here are some examples of negative sentences:
- I am not hungry – I am not hungry
- He is not busy
- The room is not big – the room is not big
Interrogative form

To form an interrogative form, you need to put the appropriate form of the verb (am, is or are) at the beginning of the sentence:
- Are you Peter? -Are you Pete?
- This room? – Is this a room?
- Are you hungry? -Are you hungry?
- He is busy? – Is he busy?
- To understand how verbs live in the English language, let’s first remember at least one Russian verb in its initial form, for example, the verb “to live”. As you know, Russian verbs in the initial form end in “-т”, and later, when conjugated, the ending changes. As for the English language, the verb in its initial form is used together with the particle to, for example, we say to be – would t, find t Xia, i.e. if the particle to precedes the verb, this means that the verb is in the initial form, and when further use verbs with persons, this particle is omitted. Let's give an example: “To be or not to be” - there are two verbs in the sentence - and both are in the initial form, and they must be used together with the particle to, and, accordingly, we will translate into English as “to be or not to be”. If we have before us the sentence “I (am) a student,” i.e. we have changed the verb to suit the person of the subject, then the particle to is omitted and the proper form of the verb is used, in this case am.
- Unlike the verb to be, other verbs in English are not conjugated, for example, the verbs “live, sit, love” in the initial form are translated into English “to live, to sit, to love”, i.e. with a particle to, and when conjugated - without to, for example, “I live, sit, love” will be translated into English as “I live, sit, love,” i.e. initial form of a verb in English without a particletonot used, but when conjugatedtofalls. The initial form in English is called the Infinitive - Infinitive.
More about the particle to watch our video tutorial:
Verb conjugations tobe in present time
Now let's learn how the verb to be changes (conjugates) in the present tense. As mentioned above, in Russian, sentences like “I am a student, she is a doctor, we are workers” are formed without a predicate verb. But to translate these sentences into English, you need to put the appropriate form to be after the subject - “I am a pupil, she is a doctor, we are workers.”
Please note the translation of the following sentences in affirmative, negative and interrogative forms into English:

Verb conjugations tobe in past and future tense
In the past tense, the verb to be has two forms - was and were (was, was, were)

In the future tense, the verb to be is conjugated as follows

Note: In modern English the form shall is rarely used to form the future tense of verbs (although its use is not a grammatical error), the form is used for all persons will. Therefore, sometimes there are discrepancies in different textbooks.
To summarize, consider the following table:

Here are some commonly used verb expressions: to be which you should learn and conjugate yourself using the conjugation table:
- To be happy/unhappy – to be happy/unhappy
- To be glad - to be joyful
- To be hungry/to be full up– to be hungry/full
- To be fond of - to love, be carried away by something
- To be busy - to be busy
- To be late (for) - to be late (for)
- To be in time for – to be on time
- To be present at – to be present at (for example, in a lesson)
- To be absent (from) – to be absent
- To be married – to be married
- To be single - to be single / not married
- To be lucky - to be lucky
- To be ready (for) - to be ready (for, for example, a lesson)
- To be afraid (of) – to be afraid
- To be interested (in) - to be interested in something
- To be ill / well - to be sick / to feel good
- To be angry (with) - to be angry, angry (at someone)
Let's conjugate together the expression to be married in affirmative, interrogative and negative sentences. What did you get?

Today we will learn about perhaps the most common verb in the English language - the verb - to be - to be, to be, to appear.
How to conjugate a verb in 3 tenses
- 1.Present tense
- 2.Past tense
- 3. Present tense
|
Present tense |
Past tense |
Future |
|
|
am I am |
shall/will |
||
|
are he is |
|||
|
is he, she, it is |
|||
|
are you, you are |
shall/will |
||
|
are we are |
|||
|
are they are |
In Russian the verb to be, to be, to be may not be used:
For example:
- 1. I am a student (instead of I am a student)
- 2. I am a girl (instead of I am a girl)
- 3. I am a boy (instead of I am a boy)
The presence of the verb to be is required!
But in English presence of verbtobeNecessarily! Even if the sentence cannot be translated into Russian. Let's give an example:
To say “I’m a girl,” you must add the verb to be to the sentence:
“I am a girl” - which translated into English means “I am a girl.”
Let's give a few more examples for understanding:
- 1. I am 20 - I am 20 (I am 20)
- 2. It is an animal - This is an animal (This is an animal)
- 3. I am singer - I am a singer (I am a singer)
- 4.She is Masha - Her name is Masha (She is Masha)
English also uses shortened forms of verbs. Let's give a couple of examples:
- 1. I am = I "m
- 2. She is = She"s
- 3. You are = You"re
- 4. She is not = She isn't
- 5. They are not = They aren't
To be in interrogative sentences
Let's look at another difference between the Russian and English languages. In Russian, affirmative and interrogative sentences differ only in sign. Let's give an example:
They are students - a statement.
They are students? - question.
Another small difference between affirmative and interrogative form in Russian this is of course a questioning intonation.
In English, an affirmative and interrogative sentence can be said with the same intonation. And in order to distinguish between interrogative and affirmative sentences, the English completely change the order of words in the sentence:
- 1. She is a nice - She is beautiful.
- 2. Is she a nice? - She's beautiful?
And in order to ask a question, you need to change the auxiliary pronoun she and the verb is (tobe) in places.
To be in negative sentences
Also in Russian the particle “not” is used to express negation, and in English the particle “not”. Let's give a couple of examples:
- 1. She is not (isn`t) at home - She Not Houses.
- 2. They are not (aren`t) enemies - They Not enemies.
Now, to consolidate everything we have learned, consider the table of changes in forms of the verb to be.
Table of changes in forms of the verb To Be
It is also worth adding that the verb to be as an independent verb it is usually used to denote the age of people, the size of objects, the price of goods, time, weather, characteristics of people.
And as an auxiliary verb to be used to form long times and passive voice(am/is/are/was/were).
That's how we learned the independent/auxiliary verb tobe in English today!
Need help with your studies?
Previous topic: Adjectives to describe people: to describe appearance and characterNext topic: Days of the week and general questions: rules and examples
The verb be in English plays many roles: a linking verb, an integral part of the predicate, part of a temporary construction, independent and modal verb. In some cases, in oral and written speech it can be used in an abbreviated form.
Conjugation of to be by tense
In the present tense, regardless of whether it is used given verb as a semantic or part of a grammatical structure, to be has 3 forms:
- am in the 1st person singular;
- is in the 3rd person singular;
- are in the plural.
I am a generous person. - I'm a generous person.
He is a generous person. - He is a generous person.
We are people generous. – We are generous people.
The pronoun you is used both in the singular and in the plural, but in any case they are added to it.
You are young enough to take up sport. – You are young enough to take up sports.
You are to come to school at 9 tomorrow. – Tomorrow you must come to school at 9.
The verb to be in the present tense can only be shortened in affirmative sentences. The full and short forms of the verb be are used equally in this case, without changing the meaning of the phrase.
I'm a generous person.
He's a generous person.
We're people generous.
The verb be is classified as an irregular verb, so its second form is used in the past tense. IN singular was (was), in the plural were (were).
Kate was at the hospital when her friend called her. – Katya was in the hospital when her friend called her.
The Ivanovs were in Moscow last weekend. – The Ivanovs went to Moscow last weekend.
According to correct use was/were in oral speech and in writing, these forms cannot be shortened.
Table Forms of the verb to be
Learn more about the use of be in the present and past tenses in different types A table will help you with your statements.
TOP 2 articleswho are reading along with this
| Time | Type of utterance | Full form | Short form | Translation |
| Present | Statement |
I am busy at the weekend. He is a talented painter. She is a good mother. It is our lovely cat. We are from London. You are good at Maths. They are famous sportsmen. |
I'm busy at the weekend. H's a talented painter. She's a good mother. It's our lovely cat. We're from London. You're good at Maths. They're famous sportsmen. |
We were busy over the weekend. He is a talented artist. She's a good mom. This is our favorite cat. We are from London. You are good at math. They are famous athletes. |
| Negation |
I am not busy at the weekend. He is not a talented painter. She is not a good mother. It is not our lovely cat. We are not from London. You are not good at Maths. They are not famous sportsmen. |
I'm not busy at the weekend. He isn't a talented painter. She isn't a good mother. It isn't our lovely cat. We aren't from London. You aren't good at Maths. They aren't famous sportsmen. |
We weren't busy on the weekend. He is a mediocre artist. She's a bad mom. This is not our favorite cat. We're not from London. You're bad at math. They are unknown athletes. |
|
| Question |
Am I busy at the weekend? Is he a talented painter? Is she a good mother? Is it our lovely cat? Are we from London? Are you good at Maths? Are they famous sportsmen? |
——————————– |
Were we busy over the weekend? Is he a talented artist? Is she a good mom? Is this our favorite cat? Are we from London? Are you good at math? Are they famous athletes? |
|
| Past | Statement |
I/He/She/It was at the football match last year. We/You/They were at the football match last year. |
——————————— |
I (He/She/It) was at a football match last year. We (You/You/They) were at a football match last year. |
| Negation |
I/He/She/It was not at the football match last year. We/You/They were not at the football match last year. |
I/He/She/It wasn’t at the football match last year. We/You/They weren’t at the football match last |
I (He/She/It) didn't go to the football match last year. We (You/You/They) weren't at the football match last year. |
|
| Question |
Was I/he/she/it at the football match last year? Were we/you/they at the football match last year? |
——————————— |
Did I (He/She/It) go to a football match last year? We (You/You/They) went to a football match last year? |
What have we learned?
The verb to be has 2 forms in the past tense. To be can be shortened in affirmative sentences of the present tense, where this verb is presented in 3 variants.
Test on the topic
Article rating
Average rating: 4.8. Total ratings received: 99.
Your application is accepted
Our manager will contact you soon
Close
There was an error sending
Send again
One of the first questions that students ask their English teacher in class: What is verb to be and why is it needed?
The verb to be is one of the most frequently used verbs, as it can act as a semantic, auxiliary, modal and connective verb. The meaning of the verb to be is "to be, to be". Unlike others English verbs, the verb to be is conjugated (that is, it changes according to persons and numbers).
Conjugation of the verb to be in the Present Indefinite tense ( Present Simple)
Today we will talk about the verb to be in the Present Indefinite tense as a semantic or independent verb, which acts as a linking verb in a sentence. Unlike the Russian language, in the English language the linking verb is never omitted, since English sentence has a strictly fixed word order: subject ( subject) + predicate ( verb) + addition ( object).
Verb to be does not change according to the rules, its forms must be remembered. In the Present Indefinite tense, the verb tobe varies depending on the number and person in which the subject appears, and has three main forms am, is, are.
Affirmative sentences with the verb to be
I am happy I (am) happy You are happy You (are) happy He is happy He (is) happy She is happy She (is) happy It is happy It (is) happy We are happy We (are) happy You are happy You (are) happy They are happy They (are) happy

Examples of affirmative sentences with the verb to be in the Present Indefinite tense:
I am in the room. I'm in the room. The book is on the table. The book is on the table. I am a doctor. I am a doctor. (I am a doctor.)
Negative sentences with the verb to be in the Present Indefinite tense:
I am not happy I am not happy You are not happy You are not happy He is happy He is not happy She is not happy She is not happy It is not happy It is not )happy We are not happy We are not (are) happy You are not happy You are not (are) happy They are not happy They are not (are) happy

Examples of negative sentences with the verb to be in the Present Indefinite tense:
I am not a doctor. I am not a doctor. The weather is not bad. The weather is not bad. They are not from Paris. They are not from Paris.
Interrogative sentences with the verb to be in the Present Indefinite tense:
For education interrogative sentences With verb to be it is enough to swap the subject and predicate, that is, the personal form of the verb to be will appear before the subject
Am I happy Am I (am) happy? Are you happy? Are you (are) happy? Is he happy? Is he (is) happy? Is she happy? Is she (is) happy? Is it happy? Is it (is) happy? Are we happy? Are we (are) happy? Are you happy? Are you (are) happy? Are they happy? Are they (are) happy?

Examples of interrogative sentences with the verb to be in the Present Indefinite tense:
Is the book on the table? The book is on the table? Is the weather bad? The weather is bad? Is the book interesting? The book is interesting?
Set phrases with the verb to be
In a word, the functions of the verb as a linking verb in the Present Simple are varied. With its help, we can introduce and characterize a person, talk about the profession and our feelings, inform about the weather and location, etc. In addition, there are a huge number of common phrases that are used with the verb to be
Examples of sentences with expressions that are used with the verb to be
I am sorry. It's my fault. He is late for the meeting. Are you ready for the test? Are you ready for the test?
Often the verb to be is used in impersonal sentences, such as:
It is expensive. It's expensive It is cold. Cold. It is important to learn a foreign language. Learning a foreign language is important.
|
|
|










