There are many types of devices for early detection of fires that are part of fire alarm installations/systems, which, in turn, are elements. Various fire detectors are also integral parts of gas, water, powder detectors, without which operation today is impossible as production facilities, and public buildings.
In the vast majority of cases, point PIs are used, which determine the appearance of factors that cause a fire in a controlled area limited by its own technical characteristics, usually in the shape of a circle or sector. However, in many industrial, warehouse, and public buildings/structures that have a large height, width, and length, they are not applicable, because this excludes their capabilities and restrictions on use.
In such cases, to protect objects, specialists from design organizations provide for the use of linear PIs, which can detect the appearance of heat and smoke in a straight section/area of the room, even over a considerable length.
Devices that are very similar in purpose, only to protect the property of citizens/organizations from theft, are linear security detectors designed to monitor unauthorized crossing of the perimeter, the active detection zone.
Types of linear fire detectors
To them on the basis of the definition that establishes the design standards of APS, ASPT; It sounds like a linear fire detector (smoke, heat) is an IP that responds to signs of fire in an extended protected area, there are two types of such technical devices:
- Linear smoke detector (IPDL) is a product that transmits an IR beam through a device/sensor that is sensitive to the transparency of the air in a protected room/building. If smoke occurs that exceeds the set threshold value, the optical detector will operate, transmitting an alarm signal to the receiving equipment of the APS installations, control and triggering devices of the ASPT. In many ways, it is precisely due to the thin, straight line of the IR beam and the location of the transceiver devices exactly on the same axis that such types are called linear IP.

- In addition, they are divided into two types - two- or one-component systems. The first is the traditional layout of the product, consisting of two devices: transmitting a continuous optical signal, and receiving it on the opposite side of the room. The second is when the transmitting and receiving parts are made in a single housing, and the transmitted IR beam is directed to a passive reflector/reflector, precisely fixed in place opposite the device. Such linear detectors with reflector are more modern devices, requiring lower costs for laying substation cables and configuring products.

- Heat detector linear (IPLT) also has several varieties depending on the type of temperature-sensitive cable used in this product. They can be contact, electronic, mechanical or optical, and for all of them the main purpose is to fix a threshold or differential increase in temperature along the entire length of the thermal cable. It is worth considering them separately.
- Contact. In them, the temperature-sensitive elements consist of several conductors in fusible insulation.
- Electronic. They are based on changes in electric current under the influence of heat. Here, thermoelements are many sensors as part of a multi-core cable.
- Mechanical. The sensitive element is a metal tube filled with compressed gas, the pressure of which increases as the external temperature rises, which is detected by the sensor of the electronic unit, which transmits a signal to the device.
- Optical. They use fiber optic cable, physical characteristics which also changes when heated.
For more information on the topic, watch the video
Among the line of models of linear heat and smoke IP products, many manufacturing companies have products designed to protect premises in buildings/structures with high temperatures.
Many specialists from design organizations, fire departments, and installation companies believe that linear individual entrepreneurs can be classified as linear; because, although their active zone for detecting fire origin factors is sectoral, the main indicator is the detection range, which for some models is up to 80 m, and this is comparable to the technical characteristics of smoke linear IP.
Pros and cons of linear detectors
The main advantage of linear IP is the ability to protect with them those objects where the use of point detectors is difficult, if not impossible, due to design features buildings/structures, technological process, specific installation locations in the premises:
- Smoke. Installation in buildings with large construction volumes, internal, undivided spaces, such as assembly and other workshops of various industries in industrial facilities, warehouse complexes, logistics centers, exhibition and sports facilities, as well as museum institutions, architectural monuments, where the installation of traditional heat and smoke power supplies on the ceilings is impossible or unacceptable for various reasons. In addition, IPDLs are more sensitive to black smoke and have a high response rate to the appearance of pyrolysis products in the air.
- Thermal. IPLT can be installed where installation of point analogues is impossible - in technological galleries, cable tunnels, ventilation ducts, etc. engineering communications buildings/structures, in other areas difficult to access/maintain regularly; as well as to protect various equipment, even if the surrounding air environment is characterized by constant high levels of dust, gas contamination, humidity, and chemical aggressiveness.
- Flame sensors installed to protect technological equipment located on the external sites of industrial enterprises, incl. for work in harsh climatic conditions.
The disadvantages of linear detectors include the high cost of the kit, which, however, pays off due to the fact that one product replaces several, or even more than a dozen smoke and heat IPs based on the protected area of the room.

Types of linear detectors
Among the products sold today on the market of components for alarm systems, the following models should be highlighted, characterized by good technical characteristics, reliability, ease of maintenance, and maintainability:
- IP-104/IPLT from the FlameStop company (Moscow) with a possible length of up to 3 (!) km. Temperature response range from + 68 to 185℃. Thermal cable is a twisted pair with a steel core coated with copper and tin. The main shell is PVC, protective for various modifications - nylon (for outdoor installation, aggressive environments), polypropylene (for chemically active areas), in steel braiding - for protection from damage. Resistant to external temperatures up to + 125℃. Diameter – from 3.6 to 4.5 mm depending on the outer shell. Weight – up to 20 kg/1 km. Protected from electromagnetic interference.
- IP-104 “Granat - thermal cable” produced by the Spetspribor company (Kazan). The maximum length of use is up to 2 km. Operation temperature – from 68 to 180℃. The maximum width of the protection zone is up to 7.6 m, the recommended width is up to 5 m. The outer diameter is 5 mm.
- IPLT XCR from Pozhtekhnika Group of Companies (Moscow). The used length of the IP is up to 1220 m. The outer diameter is 4 mm. The outer shell is made of fluoropolymer, resistant to aggressive chemical environments.
- Thermal cable PHSC-155-ECP from Protectowire. The length of the plume is up to 2 km. Diameter – 4 mm.
- IPDL D/II-4R. The most common fire detector of this type, produced for more than two decades by NPF Poliservis from St. Petersburg, consisting of two blocks - an IR transmitter and a receiver. Range – up to 150 m. Protection – IP
- IPDL-52M produced by IVS-Spetsavtomatika. A single-component linear detector, which includes a transceiver unit made in one housing and a reflector. Range – up to 80 m, width of the protection zone – up to 9 m.
- IP 212 "Trion-L2-MK" of the "SMD Company" is intended for the protection of explosion- and fire-hazardous premises. Controlled area – up to 900 sq. m. Protection – IP
- IP 212-125 (6500R) from the SensorSystem company. Single-component device of a new generation. Operating range – up to 70 m. Protection – IP
- Arton-DL. Linear single-component smoke IP with a range of up to 100 m.
- IPDL-EX. Manufacturer: NVP "Bolid". Two-component device designed for installation in hazardous areas. The range of this linear detector is up to 150 m.
In addition to these models/brands, there are many more on the fire-fighting equipment market. various products, so for optimal choice it is necessary to proceed from the characteristics of the premises of buildings/structures, external installations/equipment, upcoming conditions of installation, operation and further maintenance.
Linear fire detectors: thermal, gas, combined
Rules for installation and indoor installation
The standards for installing linear power supplies are set out in SP 5.13130.2009, in particular with regard to IPDL:
- Detectors must be placed in such a way that there are no different objects between the devices, even temporarily.
- Installation of linear fire detectors in a room with a height of more than 12 m should be carried out in two tiers.
- Installation of IPDL when protecting an area/room with two or more products should be carried out so that the distance between them is no more than 9 m, and from the wall - no more than 4.5 m.
The designation of a linear fire detector depends on the type of IP - thermal, smoke, flame.
Laboratory studies have established that linear detectors are significantly superior in sensitivity and response speed to both thermal and smoke traditional detectors.
As a rule, this does not at all mean the preference for choosing IPLT/IPDL instead of targeted IP. Each type has its own tasks, determined both by technical characteristics and the upcoming places of installation, operation and maintenance, which is always taken into account during development design and estimate documentation, including the cost of various products.
In practice, large facilities use several types of fire detectors, both point and linear, which is facilitated by the possibility of connecting them to the same control and control devices, for example, produced by the Bolid company.
Linear heat detector (thermal cable) manufactured by Protectowire (USA) is a cable that allows you to detect the source of overheating anywhere along its entire length. The thermal cable is a single sensor continuous action and is used in cases where operating conditions do not allow the installation and use of conventional sensors, and in conditions of increased explosion hazard, the use of a thermal cable is the optimal solution.
The Protectowire Linear Heat Detector consists of two steel conductors, each of which is insulated with a heat-sensitive polymer. Insulating-coated conductors are twisted to create mechanical stress between them, then covered with a protective sheath and braided to insulate them from the elements. environment.
Operating principle of a thermal cable
The principle of operation of a thermal cable: when a threshold temperature is reached, under the influence of pressure from the conductors, the insulating coating made of a heat-sensitive polymer is destroyed, allowing the conductors to come into contact with each other. This occurs at the first overheating point along the thermal cable route. To trigger the signal, you do not need to wait for a section of a certain length to heat up. The Protectowire thermal cable is a maximum heat detector and therefore allows an alarm to be generated when a temperature threshold is reached at any point along the entire length of the cable.
Technical characteristics of the Protectowire thermal cable:
- High sensitivity throughout
— Four temperature ranges
— High resistance to humidity, dust, low temperatures and chemicals
— Indispensable in hazardous areas
— Easy to install and configure
- Economical, no operating costs
— If necessary, expansion is simply added to the system
- Does not require maintenance. Expected service life over 25 years
Currently, there are several types of Protectowire thermal cables, differing from each other in the model type and the material from which the outer protective braid is made, for use in the most different conditions environment.
Criteria for choosing a thermal cable model for different temperature ranges:
| Temperature range: | ||||
| Basic | Intermediate | High | Ultrahigh | |
| Response temperature: | 68.3°C | 87.8°C | 137.8°C | 180°С |
| Minimum ambient temperature: | -44°С | |||
| Maximum ambient temperature: | up to 37.8°C | up to 65.6°C | Up to 93.3°C | up to 105.0°С |
| Standard, multi-purpose: | PHSC-155-EPC | PHSC-190-EPC | PHSC-280-EPC | PHSC-356-EPC |
| Abrasion and chemical resistant: | PHSC-155-EPR | PHSC-190-EPR | PHSC-280-EPR | PHSC-356-EPR |
| Combined, for two response temperatures: |
PHSC-68/93-TRI: Low pre-alarm temperature 68.3°C; high pre-alarm temperature 93.3°C |
|||
| Special, for low temperatures up to - 57°C: |
PHSC-135-XLT: Maximum set temperature ambient temperature up to 37.8°C; Operation temperature 57°C |
|||
Main applications of Protectowire thermal cable:
Protectowire thermal cable is used as a fire detector in systems fire alarm And fire protection. The use of thermal cables is optimal and effective in various hard-to-reach, dangerous, industrial areas. Buy a thermal cable possible in our company - .
 Objects for which the use of a thermal cable is recommended:
Objects for which the use of a thermal cable is recommended:
cable routes;
tunnels;
warehouses;
power plants;
escalators;
elevators;
open storage shelving;
conveyor conveyors;
elevator shafts;
garbage chutes;
dust collectors;
flights of stairs;
bridges and piers;
aircraft hangars;
other facilities in the petrochemical, coal mining, steel, transport and explosive industries.
Thermal cable is easily added to any automatic fire alarm system. To do this, it is necessary to have a control device with dry contact type inputs. The thermal cable has a Russian certificate fire safety and its application in the territory Russian Federation regulated by NPB 88-01.
There are a huge variety of cable products. But among them there is a special class that is used as a fire detector in fire and burglar alarm, in hardware and software systems for monitoring the condition of nuclear power plants. It was called: linear thermal fire detector. Its sensitive element is located along the entire length of the cable and is capable of changing its electrical parameters from changes in the external environment. They are so noticeable that they can be clearly recorded. Compared to others, sensor cables, as they are also called, are not unified; no standard has been established for them.
Often, in the CIS, the term “thermal cable” is used instead of the expression “linear heat detector”. This is due to the fact that for the first time it entered the Russian market under this name.
Application area
The problem of fire safety of many objects is complicated due to their complex configuration, working conditions, temperature conditions and many other factors. For example, in conditions of strong electromagnetic fields, heavy smoke, and high background radiation, most temperature, smoke and flame detectors cannot respond correctly to an emergency situation. In many cases, the use of thermal cables is justified, but in some there is no alternative to them, as is the case with nuclear reactors.
Thermal cables can be used almost anywhere, but they are especially effective in cable routes, collectors, elevator shafts, garbage chutes, tunnels, air ducts, tanks with fuels and lubricants, transformer substations. Due to the wide temperature range they can be successfully used in freezers and cold storages, elevators, warehouses, hangars, piers and many other facilities.
Since the thermal cable can be used in rooms with large electromagnetic fields without compromising its performance, it can also be used for direct control of the heating of equipment such as transformers, generators, and tomographs.
Note!
Due to the flexibility and small diameter of the cable, it is possible to control the temperature in hard to reach places installations.
In this case, it is permissible to lay the cable directly over the surface of the devices.
Operating principle of thermal cable for fire alarm
Structurally, the thermal cable is a twisted pair made of steel wire. Each wire is coated with a heat-sensitive polymer and then twisted together into a twisted pair.

Because of this, voltages arise in the cable, which, if the insulation is broken, lead to a short circuit.
The principle of operation of a thermal cable for a fire alarm is that when a certain temperature is reached, the heat-sensitive insulation is broken, the wires are connected under the influence of internal voltage, and a short circuit occurs. For the thermal cable to operate, it is enough for overheating to occur in one place. The total resistance of the line changes. A special controller measures the conductivity of the cable, calculates the location of the fire, compares it with presets and sends an alarm signal to the fire protection control panel.

Types of linear sensors
Linear heat detectors(thermal cables) according to the sensor response are divided into maximum, which respond to the achievement of a threshold temperature, differential, triggered by a certain change in temperature, and maximum-differential sensors, which respond to both. They are mechanical, contact, electronic and optical.
- Mechanical
Such sensors use the dependence of pressure on ambient temperature as a controlled parameter. The sensor is a copper tube containing compressed gas. An increase in temperature causes a change in pressure in the tube, which is detected by a sensor. The measuring unit converts the detector readings into temperature and, if threshold values are exceeded, sends an alarm to the fire panel. Practically not used due to labor intensity and the emergence of more modern and efficient sensors.
- Contact
The sensor of such a linear detector is a twisted pair of steel wires coated with a heat-sensitive polymer. The number of wires may be more than two. The outer shell is designed differently depending on the application.
In the fire or heating zone, the cable insulation melts and a short circuit occurs. The processing interface module calculates the change in line resistance and reports the distance to the fault.
- Electronic
Unlike contact linear heat detectors, linear electronic sensors do not lead to a short circuit; they record changes in sensor resistance based on temperature and transmit them to the control and measuring unit. The sensitive element consists of many sensors built into a multi-core cable, through which all information from each element of the line is transmitted. The receiving unit converts the received signals and compares them with the alarm parameters stored in its memory. If these limits are exceeded, the device issues an alarm to the fire panel.
- Optic
The operating principle of an optical linear sensor is based on a change in the optical transparency of the sensor depending on changes in temperature. A fiber optic cable is used for this. When light from a laser hits an area of fire, some of it is reflected. The processing device determines the power of direct and reflected light, the rate of its change and calculates the value of the temperature change and the location where it occurred.
Depending on the type of optical fiber and the processing module settings, the device can perform all types of thermal fire detector functions.
TOP 5 thermal cable models
The most common models of thermal cables on the Russian market:
- Protectowire,
- Thermocable
- Pozhtechnicians,
- Special device
- Etra-special automation.
Protectowire has been on the market for over 10 years. The first four manufacturers produce thermal cables for contact-type fire alarms.
Characteristics and prices are approximately the same, the difference in cable resistance is 1 meter, maximum permissible length, voltage direct current and operating range. Depending on the project requirements, it is convenient to choose best option cable.
Etra-Spetsavtomatika produces linear electronic type detectors. They are a 24 m long cable with temperature sensors mounted inside the braid; some models have presence sensors carbon monoxide. Unlike contact linear sensors, they operate as all-mode heat detectors.
Installation and connection errors
The thermal cable is subject to the same requirements as a conventional point heat sensor with normally open contacts. Installation of the fire alarm thermal cable must be carried out using proprietary fasteners developed by the manufacturer or recommended by him. This is necessary to prevent damage to the cable insulation and, accordingly, false operation of the system. If the cable consists of several pieces, then special terminal connectors are used.
The cable is laid under the ceiling or along the walls. Where installation is difficult, a suspension cable is used.
The cable is laid in a snake.
When laying it is necessary to take into account technological features object. For example, in warehouses it is necessary to take into account the operation of loading and unloading equipment.
Cable installation must be carried out with some tension at temperatures not lower than -10° C, but the system will also work in the range -40° C +125° C. When laying on flat ceilings, the distance between cables, according to international standards, should not be more than 10 .6 m for TN68 and TN88. For TN105 the distance should not exceed 7.5 m.
In addition, there are manufacturer requirements. For reliable operation, all of them must be fulfilled. If the cable touches any objects, it will interfere with the system's accurate and correct response. They can play the role of a radiator, thereby introducing an error into the work.
Conclusion
Its safety and performance largely depend on the correct design and installation of the fire protection system of an object. Role technical means detection and prevention of fire, its primary sensors, increases significantly. The requirements for them are increasing. The emergence of new detectors operating on different principles for detecting fires contributes to early and accurate fire detection.
A linear thermal fire detector (thermal cable) is necessary to search for the source causing overheating along the entire length of the circuit. T-operating 68°С (A3), t-operating -60…+46°С, D-external 4 mm, red, fluoropolymer
Heat detector linear thermal cable IPLT 68/155 XCR:
The principle of operation of a thermal cable is to melt the insulating layer under the influence of high temperatures, with further short-circuiting of the cores. A special feature of the thermal cable is that it fixes the thermal load on any part of the circuit, which allows you to issue an alarm when a certain temperature is reached anywhere in the cable, without waiting for it to heat up along its entire length.
The XCR series thermal cable has a high-strength sheath made of a material such as fluoropolymer. This shell emits significantly less smoke and gas, which makes XCR series detectors more suitable for sites with increased environmental requirements.
- Operation temperature: +68°C;
- Maximum cable length: 1220 meters";
- Operating temperature range: -40°C...+46°C;
- Continuous action of the thermal cable;
- Can be used where there are difficulties with installing classic fire detectors;
- Can be used in explosive objects;
- Has a fire-resistant and moisture-resistant shell;
- Gives an alarm when a certain temperature is reached
A wide range of devices allows you to choose a model to suit any request and functionality. A large selection will please companies engaged in the installation of fire and security alarm systems and their Customers.
Technical characteristics of IPLT 68 155 XCR
| PARAMETER NAME | PARAMETER VALUE |
| Response temperature | +68°C |
| Twisted pair resistance | 0.656 Ohm/m |
| Twisted pair capacity | 98.4 pF/m |
| Twisted pair inductance | 8.2 µH/m |
| Maximum operating voltage | 40 V |
| Maximum cable length | 1220 m |
| External diameter of thermal cable | 4 mm |
| Operating temperature range | -40°C...+46°C |
| Equipment: |
|
- Protection of explosive objects;
- Alarm system for office;
- Fire alarm for cafes and clubs;
- Alarm in the store;
- Fire systems for warehouses and office premises;
- Autonomous fire alarm for an apartment, house or cottage;
- Fire alarm for covered parking lots, garages and parking lots;
- Comprehensive fire protection for government institutions (kindergartens, schools, other educational institutions)
When choosing, pay special attention to carefully studying the technical characteristics, choosing suitable security detectors, fire detectors, and special cable products. IPLT line models are one of the best in terms of price-quality ratio and are recommended for use in systems security and fire alarm system wide spectrum.
Analogues of IPLT 68 155 XCR and other devices with similar characteristics:
Buy and order delivery of fire alarm systems in Moscow:
Linear thermal detector (thermal cable) IPLT 68/155 XCR, as well as other products (their analogues, detectors, control devices) you can order and buy in our online fire alarm store or order delivery and professional installation services in your premises in Moscow at the ABars company. (Attention, delivery is free for orders over 60 thousand rubles).
This article makes an attempt to explain in as much detail as possible the structure and principle of operation, as well as the methods and scope of application of a linear thermal fire detector (thermal cable) in automatic fire alarm systems and in automatic installations fire extinguishing
Chief Project Engineer of ASPT Spetsavtomatika LLC
V.P. Sokolov
At enterprises of the oil and gas complex, in metallurgical and chemical production, in cable collectors and channels, transport and technological tunnels when creating automatic fire alarm systems and fire extinguishing systems, one often has to deal with difficult operating conditions for this equipment. Explosion and fire hazardous areas, the presence of moisture, abrasive dust, increased pollution, low temperatures or sudden temperature changes, as well as aggressive environments dictate strict requirements for automatic fire detectors and their selection.
According to the operating conditions of automatic fire alarm system equipment, all protected objects can be divided into:
— for objects with normal operating conditions;
— for facilities with difficult operating conditions;
- for special objects.
Normal operating conditions include interior spaces protected object, which are heated during the cold season. There is no dust, presence of aggressive media and abnormal heat sources.
Objects with severe operating conditions are objects with negative temperature differences, both negative and high positive, with the constant presence of condensation due to temperature and humidity changes, with increased dust (solid, abrasive and water suspension) and objects with aggressive environments.
Special objects are objects that have explosive operating conditions.
The unique design of the linear thermal fire detector (SafeCable LHD thermal cable) allows it to be used to protect all of the above objects without exception. It is in these conditions that a linear thermal fire detector (SafeCable LHD thermal cable) has invaluable advantages.
Operating principle of the SafeCable LHD thermal cable.
Linear thermal fire detector (SafeCable LHD thermal cable ) consists of two steel conductors made using special technology, each of which has an insulating coating of a heat-sensitive polymer. Steel conductors with an insulating coating of heat-sensitive polymer are twisted to create a spring force between them, then wrapped with insulation and braided to protect them from exposure to harsh environmental conditions. A linear heat fire detector is a cable that allows you to detect a heat source anywhere along its entire length, i.e., it is a single continuous sensor. When the critical temperature is reached, the thermistor material softens and the metal conductors begin to contact each other, thereby initiating a fire alarm. For the thermal cable to operate, you do not need to wait for a certain length of section to heat up. The SafeCable LHD thermal cable is a maximum heat detector and therefore allows an alarm to be generated when the temperature threshold is reached at any point along the entire length of the linear thermal fire detector.
SafeCable LHD thermal cable device (see Fig. 1).
Metal cores with special coating:
— steel provides tensile strength;
— copper increases electrical conductivity;
- tin for corrosion resistance.
Sensitive polymer:
- heat-responsive shell.
External coating:
- polypropylene;
- nylon.
Cable:
— the shell has different colors depending on the type of thermal cable
- outer diameter (3.2mm);
– flexible enough for installation.
There are five types of linear thermal fire detector (SafeCable LHD thermal cable), differing in temperature response threshold and having three external options protective coating, differing in physical and chemical properties.
Technical characteristics of the outer coating (shell) of the SafeCable LHD thermal cable:
— the thermal cable with a general purpose coating has a very durable extruded outer protective PVC sheath, providing reliable protection thermal cables when working in almost any environmental conditions. The thermal cable sheath has fire and moisture resistance properties, and also has sufficient flexibility at low ambient temperatures. Thermal cable with a general purpose sheath is well suited for protecting residential and commercial buildings, as well as industrial facilities;
— a thermal cable coated with polypropylene, marked with the letter “P”, has a durable outer shell that is resistant to ultraviolet radiation, is characterized by high elasticity, resistance to abrasion, resistance to atmospheric conditions and high reliability of operation at high ambient temperatures. Resistant to acids, aggressive environments, oils and petroleum products. Designed for wide application in industry;
— a thermal cable marked with the letter “N” with a coating consisting of a two-layer sheath, an inner PVC layer and an outer layer of nylon. This thermal cable is specifically designed for industrial applications, such as conveyor protection, where abrasion resistance is of greatest importance. In principle, protection against abrasive dust is provided mainly by the outer protective layer of nylon, while maintaining electrical and mechanical properties.
Technical characteristics - SafeCable LHD thermal cable
- Thermal cable diameter
- Bending radius, not less
- Maximum voltage
- Thermal cable resistance (R)
- Response temperature (°C):
- Breakdown voltage (Uv)
- Change in thermal cable resistance depending on temperature
- Minimum working length of thermal cable
- Maximum working length of thermal cable
- 3.2mm.
— 6.8kg/305m.
- 76.2mm.
— ~ 30V, = 42V.
- 0.164 Ohm/m.
— 68°, 78°, 88°, 105°, 180°
— 1000 V.
— 1% at 5 degrees.
— 0.5 m.
— 3000m.
Attention: The SafeCable LHD thermal cable is a fire detector with a normally open contact. All rules and regulations of SP 5.13130.2009 for a point heat fire detector with a normally open contact in accordance with Table 13.5 automatically apply to the thermal cable.
Copy from the set of rules SP 5.13130.2009.
13.6 Point heat fire detectors.
13.6.1 The area controlled by one point thermal fire detector, as well as the maximum distance between the detectors, the detector and the wall, except for the cases specified in clause 13.3.7, must be determined according to table 13.5 but not exceeding the values specified in the technical specifications and passports for detectors.
Table 13.5
13.6.2 Thermal fire detectors should be located taking into account the exclusion of the influence on them of thermal influences not related to fire.
13.7 Linear thermal fire detectors.
13.7.1 The sensitive element of linear and multipoint heat fire detectors is located under the ceiling or in direct contact with the fire load.
13.7.2 When installing non-cumulative detectors under a ceiling, the distance between the axes of the detector’s sensitive element must meet the requirements of Table 13.5.
The distance from the sensitive element of the detector to the ceiling must be at least 25mm.
Currently on Russian market There are several types, structurally different from each other, of linear thermal fire detectors:
— The first type is semiconductor This is a linear thermal fire detector in which the wires are coated with a substance having a negative temperature coefficient as a temperature sensor. This type of thermal cable only works in conjunction with an electronic microprocessor control unit. When any section of the thermal cable is exposed to temperature, the resistance at the points of influence changes. Using the control unit, you can set different temperature response thresholds. After a short exposure to temperature, the cable restores its functionality. The design of the thermal cable does not functionally have the ability to measure the distance to the trigger point. The maximum working length of this type of thermal cable is about 300 m.
— The second type is mechanical This is a linear heat fire detector, which uses a sealed copper tube Ф=6mm as a temperature sensor. (capillary) filled with inert gas and connected to a pressure sensor. When any part of the sensor tube is exposed to temperature, the internal gas pressure changes. The pressure sensor registers this change and transmits the signal to the microprocessor electronic unit for processing. This type of linear thermal fire detector is reusable. Structurally, this type of thermal cable is a maximum differential fire detector. Working length copper tube The sensor has a length limitation from 20 to 130 meters.
— The third type of multipoint heat fire detector is a linear heat fire detector, which uses a twisted pair of wires as a temperature sensor with thermocouples included in it at a distance of about 50 cm from each other. The operating principle of a thermal cable of this type is based on the summation of emf. from individual thermocouples. Due to the spread of heat throughout the volume of the protected room during a fire, an increase in temperature will be observed at the locations of each thermocouple. Thus, the sensor provides summation of heat dissipated throughout the room. The receiving unit converts the received signals and compares them with the alarm parameters stored in its memory and the specified temperature response thresholds. If these limits are exceeded, the device issues an alarm to the fire panel. The sensitivity of the sensor depends on the number of sensitive elements located in one room. Therefore, when designing fire alarm systems, it is necessary to take into account that the sensitivity of the detector depends on the length of its sensor. This type of linear thermal fire detector is reusable. Structurally, this type of thermal cable is a maximum differential fire detector. The length of the working part of a multipoint sensor has a length limitation of more than 300 meters.
— The fourth type is optical This is a linear thermal fire detector that uses a fiber optic cable as a temperature sensor. The operating principle of an optical linear sensor is based on a change in the optical transparency of the sensor depending on changes in temperature. When light from a laser hits an area of fire, some of it will be reflected. The processing device determines the power of direct and reflected light, the rate of its change and calculates the value of the temperature change and the location where it occurred. This type of linear thermal fire detector is reusable. It only works in conjunction with an electronic microprocessor control and data processing unit. The maximum length of the optical sensor can reach up to 10 kilometers or more (depending on the quality of the optical fiber). This type of thermal cable requires qualified specialists for installation and maintenance.
— Fifth type electromechanical This is a linear thermal fire detector, which uses a heat-sensitive material applied to two mechanically stressed wires (twisted pair) as a temperature sensor. Under the influence of temperature, the heat-sensitive layer softens and the two conductors are short-circuited. A variation of this thermal cable is a linear thermal fire detector with three heat-sensitive conductors having different response thresholds under the influence of temperature (68.3°C and 93.3°C). Thermal cables from different manufacturers may have different internal resistance of steel conductors from 0.164 Ohm/m. up to 0.75 Ohm/m. The internal resistance of steel conductors determines the maximum possible working lengths of a thermal cable; this dimension corresponds to lengths from 1500 m. up to 3000m. Due to the presence of internal resistance of the conductors, it became possible to measure the distance to the trigger point of the thermal cable under the influence of temperature. Structurally, such a device is a very sensitive electronic digital ohmmeter. But if you do not need this option, then the thermal cable can work with all fire control panels that work with normally open point fire detectors. It is this type of linear thermal fire detector (thermal cable) that we are considering in this article.
Any point taken on an electromechanical type thermal cable is an independent point thermal normally open fire detector. Thus, on one meter of fire cable we have dozens, if not hundreds, of point heat fire detectors. If you strictly follow the requirements technical specifications SafeCable LHD thermal cable, then the minimum lengths into which the thermal cable can be divided should be 0.5 m. Let's take 10m as an example. thermal cable and divide it into 20 sections of 0.5 m each. We get a fire alarm loop with twenty linear heat fire detectors (in the form of small segments). The only question is why divide it into segments and then connect it together into a whole, if the thermal cable itself carries two functions, it is a linear (multipoint) heat fire detector (sensor) and a linear cable connecting itself. This one may be more expensive, but the reliability of its operation without connections will be much higher.
At the ends of the thermal cable, it is necessary to retreat 10 cm. This is an area of incorrect operation of the thermal cable due to partial dissolution of the twisted steel conductors of the linear thermal fire detector. There is a very high probability that the mechanical twisting force will not be enough to short the conductors together.
For large lengths of the linear thermal fire detector used (SafeCable LHD thermal cable), for example, more than six hundred meters, it is necessary to take into account the internal resistance of the thermal cable itself, which must be subtracted from the terminal resistor in the fire loop. So the internal resistance of one meter of SafeCable LHD thermal cable is 0.164 Ohms, and six hundred meters will be 98.4 Ohms. If the value of the terminal resistors varies by 10-15%, which we use during installation and a terminal resistor, for example 2.4 kOhm, the value of which depends on the design of the device, plus the resistance of the thermal cable, we can get a loop break signal. If the resistance of the thermal cable is large, it must be subtracted from the terminal resistor.
The SafeCable LHD thermal cable, when the initial section is closed, when exposed to a source of fire, produces a dry contact without resistance, therefore, in order for the control panel not to issue a short circuit signal, additional resistance is necessary. Depending on the fire alarm station used, the additional resistance at the beginning of the section can range from 500 to 1200 Ohms. The additional resistor “Rd” must be subtracted from the terminal resistor of the alarm loop.
Let's look at some features of installing an electromechanical linear heat fire detector (thermal cable):
- When laying it indoors along the ceiling and walls, the thermal cable must be at least 25 mm away from any surface, excluding attachment points. so that the mounting surface does not act as a cooling radiator.
- In the case when a thermal cable is used to protect electric motors, transformers and power distribution of cable collectors, the cable should be attached as close as possible to the protected surface. Surfaces must be in contact.
- When installing a thermal cable outdoors, it is necessary to organize protection in the form of a canopy made from a 5x5mm corner. made of metal or PVC for protection against rain, snow, icicle formation, wind and direct contact sun rays, especially in the summer.
- When protecting steam rooms and saunas, hide the thermal cable in special open niches, protecting it from direct contact with hot steam or air when the heat is applied.
- Select the temperature threshold for the thermal cable to be 35 degrees higher than working temperature in the protected area and the maximum possible positive temperature outside. For saunas, for reliability, it is necessary to take 60 degrees higher than the operating temperature because the heat generation in the sauna is cyclical.
- To avoid false alarms, protect the ends of the thermal cable from moisture and other solvent or conductive fumes using appropriately protected mounting boxes.
- Due to the design features, the thermal cable is attached with a simple connecting wire or with an end-of-line resistor through terminal connections. Moreover, the terminal block in the mounting box must be rotated and be at an angle of 45 degrees to the axis of the inlet hole of the mounting box (see Fig. 2). This position prevents the steel cores of the thermal cable from being pulled out of the terminal block clamps when the thermal cable is rocked or twisted along the axis.

- The most reliable connection of a thermal cable in the installation box is to twist the steel ends of the thermal cable into rings of a certain diameter under the terminal screw (see Fig. 3). After that, this mounting box is filled with a special plastic mastic to protect the terminal block clamps from an aggressive environment. The plasticity of the mastic must correspond to the climatic conditions of work. If repairs are necessary, the mastic coating should be easily removed from the installation box.

- When attaching the thermal cable, do not apply strong mechanical tightening, so as not to mechanically trigger the thermal cable, that is, short circuit it.
- When protecting rooms with a ceiling height of more than 9 meters, the distance between parallel threads of the thermal cable is reduced to two meters (manufacturer’s recommendation). This deviation from SP 5.13130-2009 requires mandatory approval in the form of special technical specifications(STU) with local fire inspection authorities. Depending on the functional purpose of such objects, additional compensatory measures for fire protection may be laid down in accordance with fire safety requirements.
Once upon a time, the only supplier of electromechanical linear heat fire detector (thermal cable) to the Russian market was the Protectowire company. At the moment there are several such companies, including our own manufacturers of this type of fire equipment. One meter of thermal cable, depending on the manufacturer, costs from 200 to 600 rubles and more. If we consider a meter of thermal cable as a point heat fire detector, then the price seems to be not so high. But the design of the thermal cable is original because it is not only a linear thermal sensor, but also a cable that connects itself. This means that the thermal cable has its own niche in the automatic fire alarm system, where only the thermal cable can be used as a thermal fire detector.
Here are some interesting solutions for using thermal cables.
Tunnels.
Technological and transport tunnels are extremely complex engineering and technical complexes and place special demands on active fire protection systems. To ensure normal operating and maintenance conditions for the tunnel, as well as to create conditions for effective fire suppression in emergency situations (ES) and emergency evacuation of people, a whole range of fire-fighting measures is being created in the active fire protection system. A road transport tunnel means extreme operating conditions for firefighting equipment, a large crowd of people and cars (human factor), low temperatures in winter, variable humidity, dust, an aggressive environment from exhaust gases, vibration and other man-made influences. That's why the best solution For any transport tunnels there is a thermal cable. As an example, we can take the Lefortovo and Gagarin tunnels in Moscow, which are already protected by an electromechanical thermal cable. In automobile tunnels, a linear thermal fire detector is installed on the ceiling directly above the roadway in accordance with the requirements of the rules SP 5.13130-2009. The cable manifold and cable risers are also protected with a thermal cable. The choice of the type and temperature of the thermal cable is determined by the technical conditions.
The thermal cable in the tunnels is secured using steel cables stretched along the roadway. Due to low temperatures and the formation of ice, constant drafts and wind, the cable with the thermal cable may swing, so Special attention It is necessary to pay attention to securing the cable in the installation box. We have already talked about this above. Depending on the season of heat or cold, the cable may sag or shorten. In order for the tension to always be the same, it is necessary to use a device in the form of a metal weight that pulls the cable through a small pulley. The load must be in a special receiving cup that prevents the load from accidentally falling down.
Next to the Gagarinsky road transport tunnel there is a railway transport tunnel. Another problem arose there. Diesel locomotives run through this tunnel. The exhaust pipe of the diesel locomotive is located approximately one and a half meters from the ceiling of the tunnel. As it turned out, the exhaust gases from it have enough high temperature up to 400°C., which could lead to false alarm thermal cable, especially when the train is moving slowly in the tunnel. The solution was found in the form of a metal corner 50x50mm. It was fixed at a short distance from the tunnel ceiling with an angle downwards. The thermal cable itself was placed inside the corner on special mount so that it does not come into contact with the surface of the corner. A metal corner protected the thermal cable from below, breaking the flow of hot air to the sides, but this did not prevent the thermal cable from operating in a real fire, when the heat from the source of the fire rose upward and filled the volume of the tunnel near the ceiling.
Entrance halls.
Large entrance lobbies of administrative buildings always pose challenges in balancing fire protection and lobby design requirements. Therefore, as a rule, false ceilings are closed tightly with plasterboard, making it impossible to make special hatches in them for servicing fire detectors. However, this space is being filled with technological equipment and especially cable networks. The fundamental solution to this issue was the use of a linear thermal fire detector (thermal cable) to protect the space of a false ceiling covered with a continuous layer of plasterboard. The ends of the sections of thermal cables protecting the false ceiling are brought to a special place where a hatch for maintenance is made, and the thermal cables are connected to the fire alarm system there. The thermal cable does not require maintenance and can be located behind a false ceiling for decades, performing its main functions of fire protection.
Aircraft parking hangars.
Hangars for parking and servicing large aircraft have a complex engineering design with huge spans and are unique and expensive objects. Water is used to protect these structures from overheating in case of fire. As an incentive system for turning on water irrigation metal structures and farms a thermal cable is used. The thermal cable is in metal pipes, and the pipes themselves are tightly pressed to the surface of the trusses or welded to them. In the event of a fire, water will be supplied to cool the ceiling structures if the metal trusses warm up to the operating temperature of the thermal cable, which is a maximum of 180°C. There is a critical temperature for the durability of metal under load, after which the metal is released and the structure begins to deform and then collapse under its own weight. This solution to use a linear thermal fire detector (thermal cable) in a pipe does not comply with the accepted requirements of SP 5.13130.2009 for the fire alarm system. This decision rather relates to the technology of protecting ceiling truss structures and the method of using a thermal cable as a thermal sensor.
Electrical diagrams for connecting an electromechanical thermal cable to fire alarm devices.
Any device that uses thermal fire detectors with normally open contacts can be used as a fire alarm receiving and control station. In projects where thermal cables with lengths of up to 3000 meters are used (for example, cable collectors or conveyors), it is effective to use special devices with digital display distance to the trigger point.
When using an electromechanical linear heat fire detector in explosive areas, in accordance with existing standards An intrinsically safe barrier must be installed between the receiving device and the thermal cable. The optimal solution for protecting such premises would be to lay a thermal cable from a room with normal conditions into the protected room and exit back. So we endure the montage electrical connections to a neutral room.
There are three options for connecting an electromechanical thermal cable to fire alarm loops:
— for two-level fire alarm loops;
— for single-level fire alarm loops;
— for polar fire alarm loops (type PPK-2, SIGNAL, etc.).
After an electromechanical linear heat fire detector is triggered by a source of fire or mechanical damage it is necessary to restore the functionality of the thermal cable. This is achieved by biting out the damaged area and replacing it with regular wire. To find the short circuit point, special instruments are used. The thermal cable is disconnected from the control panel and connected to the sound generator. Next, the specialist, using a special sensor, walking along the linear heat fire detector (thermal cable) picks up the sound signal. At the short circuit point the sound becomes continuous. The accuracy of short circuit detection is up to 1 cm. A less accurate way to find a short circuit in a thermal cable, but also the most accessible, is to measure the resistance with a conventional digital ohmmeter. The accuracy of determination in this case is within five meters.
Figures Fig-4, Fig-5, Fig-6 show typical electrical circuits connecting a thermal cable to fire alarm devices.
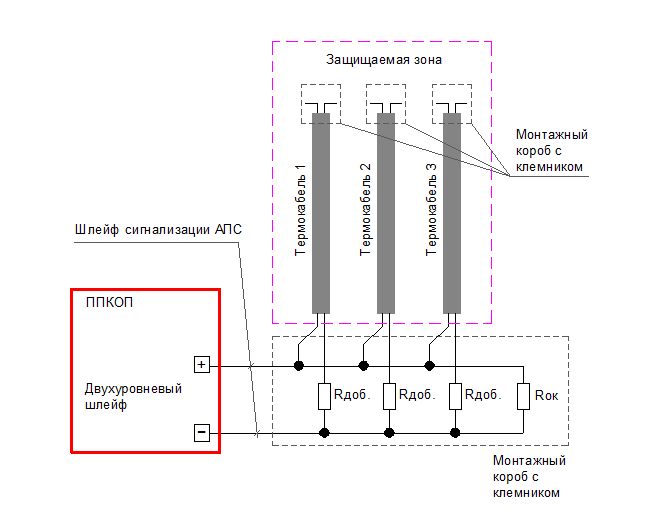
Diagram for connecting a thermal cable to a two-level fire alarm loop.

Diagram for connecting a thermal cable to a single-level fire alarm loop.

Diagram for connecting a thermal cable to a bipolar, single-level fire alarm loop.
The linear thermal fire detector (SafeCable LHD thermal cable) is easy to design, install, operate and maintain. The thermal cable has shown its reliability in operation in difficult conditions and in time. It should be noted that the need for a linear thermal fire detector (thermal cable) in the Russian market is determined by its unique capabilities in the field of fire safety.
And finally, if you have any questions about the use of thermal cables or you want to get more detailed information, the specialists of ASPT Spetsavtomatika LLC are always ready to provide assistance, as well as conduct trainings and individual project support.
Reliability and high quality are our main priority.








