§ 21. Door blocks Classification of door blocks
The door block consists of a door frame and a door leaf hung on a vertical bar of the frame on hinges.
By appointment, the doors are divided into internal ones, including entrance doors from staircases to apartments and other premises, for sanitary facilities; external (entrance to buildings); vestibule and special soundproof; fire fighting; smoke-proof, etc. Internal doors are interior, kitchen, for bathrooms, utility (for pantries, built-in wardrobes), for access to a balcony (balcony).
Doors by design are divided into frame (paneled); panel boards with solid or small-hollow filling; with threshold and without threshold; with a transom and without it. By the number of canvases, single- and double-sided doors are distinguished, including those with canvases of different widths.
According to the direction and methods of opening, the doors are hinged, swinging and sliding, and according to the presence of glazing - glazed or deaf.
In terms of moisture resistance, doors are divided into doors of increased moisture resistance, designed for rooms with a constant relative humidity of more than 60% (tambour doors and doors installed in the outer walls of buildings), and doors of normal moisture resistance - for rooms with relative humidity up to 60%.
Depending on the finish, doors come with an opaque finish (enamels, paints, decorative sheet or film materials) and with a transparent finish (transparent varnishes). In separate rooms, for lighting with the so-called "second light", a transom with a width equal to the width of the block is installed above the door.
In double-leaf door blocks, the gap formed between the canvases in the porch is closed on both sides with flashings. In doors with swinging canvases that open in different directions, the porch is not closed with a flashing.
Thresholds are installed in the blocks of external doors, which improve thermal and sound insulation. Door blocks of internal doors are made with a threshold (entrance to apartments) and without a threshold (interior).
Depending on the hinge, the doors are distinguished between right and left (Fig. 81). When installing the door block in the opening, the gap formed between the wall and the frame is caulked and covered with a casing.
For the purpose of sound and heat insulation in blocks entrance doors polyurethane foam gaskets are installed in the apartment.
Frame doors (Fig. 82) consist of vertical, horizontal and medium bars (strapping) with a thickness of 44.52 and a width of 122 mm. The gaps between the strapping bars and the mullions are filled with shields - panels, glasses. Panels can be plank (mainly in external doors), plywood, fibreboard or chipboard.
Plank panels are connected in a groove and overlap; in the latter case, the panel on the opposite side of the overlay is covered with a figured layout, which is attached to the bars with studs recessed into the wood, or with sunken screws. It is not allowed to fasten layouts to plank panels. Frame doors are mainly used as entrances from the street to the premises.
shield door is a wooden frame assembled from wooden bars with a section of 32 ... 34x40 ... 60 mm, which are connected at the corners with metal clips or on spikes (dowels), filled with a center of various designs and lined on both sides with hard fiberboard or plywood, planed veneer, paper-laminated decorative plastic, decorative PVC film, decorative paper.
The shield door is light, has good soundproofing qualities, strength, dimensional stability, hygiene, and is easy to use. A small amount of materials, mainly of low grades, is spent on the manufacture of a panel door. For residential and public buildings, panel doors are made with and without lining. The lining is attached around the perimeter to the door in the groove and ridge on three sides.
Wooden interior doors for residential and public buildings, depending on the design, are divided into the following types (GOST 6629-88): G - with blind canvases; O - with glazed canvases; K - with glazed swinging canvases; U - with a thick filling of canvases, reinforced for entrances to apartments.
Doors of G and O types are made with one- and two-leaf leaves with small-hollow (lattice) filling of the leaves, with and without a threshold, with and without overlap, with and without lining, with and without boxes.
Type K doors are made with double-leaf leaves, with small-hollow filling of the leaves, without a threshold, without overlap, with or without lining, with frames.
Type U doors are made with single-leaf blind leafs, with a threshold, without overlap, without facings, with reinforced frames or without frames. Shields in doors of this type are filled with calibrated thickness wooden slats or particle boards - chipboard, as well as strips of chipboard calibrated in width, laid on the edge. The vertical bars of the frame of this canvas must have a width of at least 90 mm, horizontal - at least 45 mm. The bars are connected in the corners with glue in a spike or on dowels, paper clips.
D  Doors used for sanitary cabins are allowed to be manufactured with a canvas 30 mm thick and at least 1800 mm high, with a box bar width of at least 50 mm.
Doors used for sanitary cabins are allowed to be manufactured with a canvas 30 mm thick and at least 1800 mm high, with a box bar width of at least 50 mm.
Doors of types O and K can be made of a frame structure with a bar width of at least 100 mm. A box without a threshold is embroidered from below with a mounting board, which is fastened with nails or with the help of tenon joints to the ends of the vertical bars.
In the doors of types O and K of public buildings, protective fences are installed on both sides of three wooden planks with a pitch of 150 mm, protecting the glass from damage.
Doors of U type and frameless types G and O are equipped with sealing gaskets made of polyurethane foam (GOST 10174-90). The design of type O doors is shown in fig. 83. Door thickness 40 mm. The filling of the panels (Fig. 84) of door panels can be solid wood, bars (slats) or chipboard strips, small-hollow wooden bars (slats) or chipboard strips with a pitch of 40 ... 60 mm, small-hollow veneer, plywood, hard or soft fiberboard, paper honeycombs.
Bars are placed in the middle of the door panels for installing the lock and handles. The length of the bars should be 400 mm for canvases 2000 mm high.
For the construction of unique buildings (theaters, museums), high-quality doors are made, lined with precious wood (oak, walnut, mahogany, rosewood) and finished with light varnish to preserve the texture. Doors of residential and public buildings are painted with oil or synthetic paints and enamels, including water-based ones.
The door frame is a frame designed to fasten door panels. Door frames come with and without a threshold. A box with a threshold is assembled from two vertical and two horizontal bars, interconnected by a spiked joint with glue and dowels.
A box without a threshold consists of two vertical and upper horizontal bars, connected with a spike joint on glue and fastened with dowels in the corners. Door leafs are hung in boxes on two hinges, and type U doors - on three hinges.
Wooden exterior doors for residential and public buildings (GOST 24698-81), depending on the purpose, there are entrance and vestibule types H, service doors - C, hatches and manholes - JI. Type H doors are made panel or frame (paneled), and panel doors can be with slatted sheathing.
D  Veri types H and C can be single- and double-sided, glazed and with blank sheets, with and without a threshold. Shield doors (cloths) must be filled with calibrated rails in thickness. When sheathing the door leafs from the outside with profiled strips on a layer of glassine or galvanized sheet steel, it is allowed to use hard fiber boards or plywood of the FK brand for the manufacture of doors. Tambour doors can be made without sheathing with wooden slats. The rails are fastened to the canvas with screws or nails 40 mm long with an anti-corrosion coating in increments of up to 500 mm. In the lower part of the H-type door leaf, they are protected with wooden planks 16 ... 19 mm thick (Fig. 85) or decorative laminated paper strips 1.2 ... 2.5 mm thick.
Veri types H and C can be single- and double-sided, glazed and with blank sheets, with and without a threshold. Shield doors (cloths) must be filled with calibrated rails in thickness. When sheathing the door leafs from the outside with profiled strips on a layer of glassine or galvanized sheet steel, it is allowed to use hard fiber boards or plywood of the FK brand for the manufacture of doors. Tambour doors can be made without sheathing with wooden slats. The rails are fastened to the canvas with screws or nails 40 mm long with an anti-corrosion coating in increments of up to 500 mm. In the lower part of the H-type door leaf, they are protected with wooden planks 16 ... 19 mm thick (Fig. 85) or decorative laminated paper strips 1.2 ... 2.5 mm thick.
Cloths and frames of fire-retardant and insulated doors of type C are sheathed with thin-sheet galvanized steel with a thickness of 0.35 ... 0.8 mm. Cloths of slow-burning doors are protected on both sides with asbestos cardboard 5 mm thick.
Doors are glazed with window glass 4 ... 5 mm thick (GOST 111-90). When installing glass at a distance of less than 800 mm from the bottom of the leaf, a protective fence (grille) is installed.
Wooden doors (GOST 14624-84) are designed for industrial buildings of industrial and agricultural enterprises. Depending on the purpose, they are divided into internal (B) and external (H). By design, the doors come with a quarter porch with blank canvases (D), with a quarter porch with glazed canvases (O), as well as with glazed swinging canvases (K). Doors are divided into panel doors with solid or lattice filling and frame doors.
Doors of G and K types are made with right or left hinged panels, with and without a threshold.
Type G internal doors have a height of 1800 and 2000 and a width of 800 ... 1802 mm, type O - a height of 2000 and a width of 1402 ... 1802 mm, type K - a height of 2000 and a width of 1408 ... 1808 mm. External doors of G and O types have a height of 2000...2300 and a width of 800...900 mm. The thickness of the doors is 40 mm. External doors are lined with solid fibreboard or plywood and must be sheathed with profiled layouts (GOST 8242-88) over a layer of glassine. The layouts are fastened with screws or nails with an anti-corrosion coating in increments of up to 500 mm. The lower part of the outer sheets is lined with a plinth made of paper-laminated plastic 220 mm wide, at least 2 mm thick or made of superhard fiberboards (GOST 4598-86), thin galvanized steel or aluminum. The sections of the outer doors of the panel structure are shown in fig. 86.
| " |
Introduction
Door blocks in an individual residential building are divided By:
- purpose - external and internal;
- production material - wooden, metall, PVC, MDF-lined or veneer;
- enclosing functions - deaf and ostek fiefs;
- the number of wings - single and double doors you are e.
Door block:
- a - single-leaf;
- b - double-leaf.
Basic requirements for outdoorny door blocks for installation in individualdual residential building - strength and highthermal characteristics. Majoritydevelopers prefer outdoordoors - insulated metal in the "deephome "execution, and internal - woodenor PVC, single or double leaf.
The table below shows the main sizes of the two ray.
Some types of doors for an individual residential building
Important characteristics of doors - noise reductionprotection, thermal protection and durability. Provide themvayut structural elements: box, doorcanvas, fittings (hinges, handle and lock),threshold and platbands.
Elements of the door block
Types of external and interroom doors
Benefits of wooden exterior doors(rice. A) - environmental friendliness, aesthetics and malight weight. Disadvantages - low heat-shieldingproperties and exposure to externalaggressive environment. Such doors requireyannogo care (painting, polishing); According tomany developers, they are less durable than metal.
Metal exterior doors (Fig. b) - the most common type of entrance todaystructures in private construction. They're upquite strong, as they have a metalframe; can be well insulated; do not requireextra care thanks to high qualitynatural paintwork, resistantto external aggressive environment.
Entrance doors:
- a - wooden;
- b - metal.
Interroom wooden doors (rice. A) made of solid wood or studdedtray, and when installed indoorsyah at home they are fully capable of providingcomfortable soundproofing.
MDF doors(rice. b) less environmentally friendly,than wooden ones. But they are not destructible.insects and fungi, although they knowsignificantly lower noise protection characteristics.As a rule, such doors are faced with veneer.or laminate, which significantly reduces the costdesign bridge compared to similarfrom an array. With good external qualitiesa significant drawback is the fear of moisture. In wetrooms (bathrooms, baths, saunas)individual residential building doors made of MDF withchange is not recommended.
When installing in the interior of the housepvc doors (rice. V) bothcomfortable sound insulation is sintered. But theiruse greatly reduces the naturalventilation, as they usually have a raftnye abutments and do not let air through. osnew advantages - durability, ease of maintenanceand durability.
Interior doors from:
- a - a tree;
- b - MDF;
- c - PVC.
Frame doors are made with claddingfrom laminate or veneer on wood or methallus frame (Fig. a, b). Internalcavities fill corrugated cardboard orinsulation, plywood is mounted on the frame orhardboard. Frame wooden doors are consideredthe cheapest.
Door designs with a frame made of:
- a - a tree;
- b - metal.
There are many implementation optionsdoors. The right designwill allow you to maintain the interior in the desired style.
Door design options
Installation of door blocks
Installation blocks doorways all types - quite difficultcapacious process, but many developersal residential buildings cope with this taskon one's own. What is remarkable: the more difficultdoor design, easier technology settingki. For example, to install sliding, warehousepuffy and similar doors are enoughinstall the supporting frame and align the verticaldesigns. Installation of the simplest designdoors - hinged - we will consider in more detail.
The installation of the door block is recommendedto sing before the finishing worktami. To begin with, you need to decide ondoor burr, box design (with thresholdor without), check the verticality of the walls in placelocation and specify the dimensions of the doorema - there must be a gap between the door frameand wall (about 10–15 mm).
Then you need to prepare a profiledtimber under the door leaf (Fig. A), consideringone of three ways to gusset it:
- with trimming the ends of the box parts by 45°(rice. b) - the simplest and easiestcue, if you have a finely tuned one at handangle cutter, without it to ensure the accuracy of the angleand matching the dimensions of the box parts underthe door leaf is quite difficult;
- with the connection of the corners of the box on the tenon(rice. V) - the highest quality, but trueexpensive method in terms of accuracy oncutting grooves and thorns, requiring a professionalonal carpentry skills;
- with trimming of the ends of the box parts by 90°(rice. G) - simpler in comparisonwith the first method in assembly accuracy and less laborious in comparison with the second.
Door frame device:
- a - profiled beam (section);
- b - connection of corners at 45 °;
- in - connection on a thorn;
- d - connection of angles of 90 °.
Following the third method, since iteven a novice in this business twists, and after completingappropriate measurements of the door leaf,cut racks. For box designwith a threshold it is necessary to providetop and bottom clearance no more than 5 mm between the edgesdoor leaf and grooves of the crossbar and threshold.That is, you should cut the beam 10 mm moredoor leaf length. For box without poroha it is necessary to provide a gap from abovenot more than 5 mm and from the bottom of the floor not less than 10 mm. That is, the rack must exceed the length by 15 mmdoor leaf.
Gaps on the sides (for a box with or without a threshold)set the same - no more than 5 mm. For thiscrossbar and threshold are cut 10 mm longerthe width of the door frame, taking into account the thicknesstimber of both racks - 50 mm. OtherIn other words, the crossbar (K) should be equal to:
K = B + 2h + 2b,
where B is the width of the door leaf, mm;
h - gaps on the sides, 5 mm;
b - thickness of two racks, 50 mm.
Next, at the ends of the racks, a cutout for the groove is marked,accurately measuring the convex part (shelfki) crossbar and threshold (Fig. A). By thismarkup carefully cut out the necessaryrecess (Fig. b). Then, building themprovisioned workbench of four stoolsthe same height at the corners of the future doorboxes, connect the ends of the racks to the thresholdand the crossbar, while the groove is combined with the shelfwhich is fixed on the screws. If the threshold is notconsidered (Fig. G), then the lower ends of the racks are temporarily fixed on the rail in compliance withappropriate width of the door leaf and forgaps on the sides. The box is ready.
Door frame assembly:
- a - the ends of the vertical and horizontal bars of the box;
- b - cut groove on the verticala bar under a shelf of a horizontal bar;
- in - a box with a threshold;
- g - a box without a threshold.
After that place the door inside the box and youequalize the gaps at the edges (Fig. A). Thenapply awnings, door lock and acceptbar at the place of their installation (Fig. b) to determine their location (Fig. V). For a mortise lock on the door leaf markthe position of the box locking mechanism and fixicutting bar. Installation location door hinges (canopies) are laid at a distance of 15–20 cmfrom the edges, and mortise locks- 85–95 cm from the floor.
Marking the door leaf and box for the installation of canopies and a mortise lock:
- a - placing the door inside the boxand alignment of gaps;
- b - attaching canopies and a castle;
- c - marking the location of the canopies and the castle.
The choice of lock depends on the purpose of the room.In interior rooms applied in the basicsnom so-called latch locks (Fig. A), designed to hold the door closedcondition. outdoors, includingand those where you need to restrict access (onfor example, furnace), locks with a locking device that are more difficult to install are usedand keys (Fig. b).
Some types of mortise locks:
- a - latch lock;
- b - locking device.
As for door hinges (canopies), the modernThe changing industry offers manyvariants of their execution, distinguished by constructure, installation methods, degree of strength and appearance.
For entrance doors and heavy doorsnyh canvases it is better to choose overhead awnings(rice. A), for light interior - loops-butterflies (Fig. b). Overhead canopies in the layerin female form have a thickness of 6–8 mm, thereforeduring installation, they must be deepened into the enddoor leaf. Butterfly loops are thickwell, about 3 mm, they are easily fixed in placeand do not require cutting.
Some types of door hinges:
- a - overhead canopies;
- b - butterfly loops.
After choosing door hinges (canopies) and mortiselocks, you can proceed to their installation. FirstIn fact, it is necessary to install the door leaf on the edge (Fig. A) and transfer the previously made markupku from the front side to the end of the door usingsquare (Fig. b). Between two linesmarkings apply a canopy (Fig. V) and an essaychime its longitudinal side (Fig. G). Having thus determined the landing site of the canopy,it is deepened to the thickness of the petal (Fig. d). To do this, you can use a chisel ormanual electric cutter. At the end of thisstages fix the hinges to the door leaf shurupees (Fig. e).
Canopy installation sequence:
- a - installation on the edge of the door leaf;
- b - transfer of markup to the end;
- in - determination of the location of the loops;
- g - delineation the longitudinal side of the canopy;
- d - deepening of the canopy for thickness petal;
- e - landing a canopy on the screws.
Next, the door leaf is installed on the oppositedown rib (Fig. A) and proceed to montazhu mortise lock. The markup you didearlier, transferred with a square(rice. b) and determine the axial (centralnuyu) line (Fig. V). Then apply contoursfixing plate, as well as the body of the lockingth mechanism, leaving allowances of 2-3 mm with eachsides (Fig. G). According to the markup, they prepare a nestunder the body of the locking mechanism and a recess under the landing zone of the locking bar (Fig. d). Further, holes are drilled on the sides of the canvasfor door handles, key holder and tiescrews in the respective areas and assemblelock at the place of the tie-in (Fig. e). Similarlatch-locks are cut in this way.
The sequence of inserting the door lock:
- a - installation of the door leaf on the edge;
- b - markup transfer;
- c - determination of the center line of the locking device and the door canvases;
- d - determining the position of the fixing plateand lock cases with allowances;
- e - preparing a nest formechanism and recesses for the fixing bar;
- e - drilling necessary holes and mechanism assembly.
In conclusion, it remains to arrange for the latch and forporn tongue entrances in a box. Forthis, a receiving bar is applied in placeinstallation, then mark the necessary nichesand deepen them. After fixing the bar and, racesputting the door leaf in the open positionnii in relation to the box (Fig. A), windowscarefully fix the canopies to the jamb beforemarked marks (Fig. b).
Work on the latch and locking tongue of the door leaf in the box:
- a - installation of the receiving bar;
- b - fixing canopies.
The door is closed and the accuracy is checked againfilling gaps between the canvas and the boxwhich, as well as the quality of the mortise lock whenopening (closing). If it is needed,perform adjustment of attachments. After that, on the upper corners and lower sidesthe door frame is stuffed with slats (Fig. A), without fear of damaging the front of the jamb -subsequently it will be closed by platbands. Suchprocedure will protect the skew of the box during thetanovki and will facilitate the installation of the door flushwith wall surfaces. If a door is built ina box without a threshold, first fix the rails,then remove the temporary bar attachedto the bottom of the racks (Fig. b).
Preparation assembled door for installation in a doorway:
- a - stuffing rails,
- b - fixing the rails and removing the temporary beam.
To install the door flush on the plasterwalls, it is necessary to insert the box andtray into the opening and press the protruding ends of the railsto Wall. After that you need to checkhorizontal and vertical arrangementdoor frame. If there are distortions, for examplemeasures horizontally, it is necessary to substitute the covens underone of the racks (if the door is without a threshold) or sidesthreshold until complete alignment (Fig. A). If the vertical is not maintained, then levelcobs between the ends of the rails and the wall. That isto tilt the door forward, substitutingyut covens under the upper slats, so that back - underends of the lower rail (Fig. b).
Installing the door in the opening:
- a - horizontal adjustment (front view);
- b - vertical adjustment (side view).
By setting correct position doors, racksthe door frame is fixed to the wall with anyfoot way. After that, remove all the railsand proceed to eliminate the gaps between the doorbox and opening (Fig. A). Fill firsteliminate voids between the box and the wall installationfoam (Fig. b). Then after dryingfoam and trim its excess from the front side towear a plaster mortar, and from the back - a deviceivayut door slope(rice. V). After thatyou can start finishing, on the windowswhich are stuffed with platbands (Fig. G).
Preparing the door perimeter for finishing:
- A - installed door in the opening;
- b - filling the voids of the mounting foam;
- c - slope device;
- g - finishing and installation of platbands.
STEEL DOOR BLOCKS
Specifications
INTERSTATE SCIENTIFIC AND TECHNICAL COMMISSION
ON STANDARDIZATION, TECHNICAL REGULATION
AND CERTIFICATIONS IN CONSTRUCTION (MNTKS)
Moscow
Foreword
The Eurasian Council for Standardization, Metrology and Certification (EASC) is a regional association of national standardization bodies of the states that are members of the Commonwealth of Independent States. In the future, it is possible that national bodies for standardization of other states will join the EASC
Under the EASC, the Interstate Scientific and Technical Commission for Standardization, Technical Regulation and Certification in Construction (MNTKS) operates, which has been granted the right to adopt interstate standards in the field of construction
The goals, basic principles and basic procedure for carrying out work on interstate standardization are established by GOST 1.0-92 “Interstate standardization system. Basic Provisions” and MSN 1.01-01-96 “System of Interstate Regulatory Documents in Construction. Basic Provisions»
About the standard
1 DEVELOPED by the Center for Certification of Window and Door Equipment and the Federal State Unitary Enterprise Central Design and Technology Bureau (FSUE TsPKTB of the Gosstroy of Russia) with the participation of the Academy of Safety and Law and Abloy Oy, the Bjerkboda plant, Finland
2 INTRODUCED by Gosstroy of Russia
3 ADOPTED by the Interstate Scientific and Technical Commission for Standardization, Technical Regulation and Certification in Construction (ISTCS) on May 14, 2003
|
Short name of the country according to MK (ISO 3166) 004-97 |
Country code according to MK (ISO 3166) 004-97 |
Abbreviated name of the state construction management body |
|
Ministry of Urban Development of the Republic of Armenia |
||
|
Kazakhstan |
Kazstroykomitet of the Republic of Kazakhstan |
|
|
Kyrgyzstan |
State Commission for Architecture and Construction under the Government of the Kyrgyz Republic |
|
|
Ministry of Ecology, Construction and Territorial Development of the Republic of Moldova |
||
|
Russian Federation |
Gosstroy of Russia |
|
|
Tajikistan |
Komarchstroy of the Republic of Tajikistan |
|
|
Uzbekistan |
Gosarchitektstroy of the Republic of Uzbekistan |
4 INTRODUCED FOR THE FIRST TIME
5 Entered into force on March 1, 2004 as a state standard Russian Federation Decree of the Gosstroy of Russia dated June 20, 2003 No. 76
Information about the entry into force (termination) of this standard and changes to it in the territory of the above states is published in the indexes of national (state) standards published in these states.
Information about changes to this standard is published in the index (catalog) "Interstate standards", and the text of the changes - in the information indexes "Interstate standards". In case of revision or cancellation of this standard, the relevant information will be published in the information index "Interstate Standards".
INTERSTATE STANDARD
STEEL DOOR BLOCKS
Technicalconditions
Steel doors Specifications
Date of introduction - 2004-03-01
1 area of use
This standard applies to steel door blocks with installed locking devices (hereinafter referred to as door blocks or products) for buildings and structures for various purposes.
The standard does not apply to door blocks for special purposes in terms of additional requirements for fire safety, explosion and bullet resistance, exposure to aggressive environments, etc., as well as to door blocks of protective cabins according to current regulatory documentation.
The scope of specific types of products is established depending on the operating conditions in accordance with the current building codes and regulations, taking into account the requirements of this standard.
The standard can be applied for certification purposes.
2 Normative references
This document makes reference to the following standards:

1 - upper locking crossbar; 2 - upper link of the main lock; 3 - web frame (welded steel profiles); 4 - places for attaching the internal "hatch"; 5 - valve; 6 - the place of attachment of the upper link; 7 - crossbar of the deadbolt of the lever lock; 8 - latch; 9 - deadbolt of the cylinder lock; 10 - lower link of the main lock; 11 - places for fastening the finish; 12 - internal cavity for filler; 13 - vertical thrust guide; 14 - lower locking crossbar; 15 - mounting "eye"; 16 - threshold; 17 - hole for anti-removable crossbar (pin); 18 - anti-removable passive crossbar (pin); 19 - mounting anchor; 20 - box (frame); 21 - combined lever-cylinder lock; 22 - inner steel sheet; 23 - outer steel sheet; 24 - loop knot; 25 - peephole
Picture 1 - An example of the design of a door unit, the leaf of which is welded from two steel sheets and steel profiles, the frame (frame) is made of a bent steel profile
Canvas with two steel sheets, steel profiles box section and honeycomb filling
Door leaf with an outer steel sheet and an inner sheet of fiberboard, with profiles of complex cross-section and filling with wood or mineral insulation

Door leaf of "bent box" type, with U-shaped steel profiles and foam filling

Door leaf with steel outer sheet and fiberboard inner sheet, steel angle profiles with timber bars and foam core
Figure 2 - Examples of door leaf designs

Figure 3 - An example of the design of a door block welded from steel sheets and profiles (with filling the middle profile of the frame and door leaf with wood and foam material)

Figure 4 - An example of the construction of a door block welded from steel sheets and profiles, with natural wood cladding

Figure 5 - An example of the design of a double-leaf door unit with a cladding made of wood or wood-based materials (horizontal section)

Figure 6 - Examples of door leaf structures welded from two flat steel sheets and steel profiles (a) and a bent box door leaf (b) with vertical reinforcing profiles


5.4 Requirements for materials and components (including gaskets)
5.4.1 Materials and components used for the manufacture of door blocks must comply with the requirements of standards, specifications, technical certificates approved in the prescribed manner.
5.4.2 Materials and components used for the manufacture of door blocks must be resistant to climatic influences.
5.4.3 The surfaces of steel elements of boxes and sheets should not have cracks, mechanical damage, pits, distortions, rust. On the front surfaces of steel elements, slight local depressions, risks, waviness up to 0.5 mm deep are allowed, which do not reduce the functional properties and quality of products.
5.4.4 Steel parts of structures should be made of steel grades that ensure the strength characteristics of structural elements, welded, bolted and other joints, depending on the nature and conditions of their work.
Steel elements are recommended to be made from steel grade not lower than StZkp2 according to GOST 380, rolled sections according to GOST 1050 or high-alloy steel according to GOST 5632.
5.4.5 Sealing gaskets must be made of weather- and frost-resistant elastic polymer materials in accordance with GOST 30778.
The fit of the sealing gaskets must be tight, preventing the penetration of water. Sealing gaskets must be installed continuously around the entire perimeter of the porch.
5.4.6 Wooden glued cladding panels must meet the requirements of GOST 30972, profile molded wooden details- GOST 8242.
5.5 Requirements for hinges, locks and other locking devices
5.5.1 In the manufacture of products, locking and auxiliary devices and hinges are used, specially designed for use in metal door blocks. Examples of designs of hinges and locks are given in the appendix.
The type, number, location and method of fastening of locking devices and hinges are set in the working documentation based on the size and weight of the opening elements of the product, as well as the operating conditions of the door blocks. Cloths of door blocks weighing more than 200 kg, as well as products used in public buildings (schools, hospitals, etc.), are recommended to be hung on three hinges. The recommended location of the middle hinge is 150 - 200 mm below the top one.
5.5.2 For hanging canvases on a box (frame), it is recommended to use overhead bearing or other hinges with the ability to adjust in different planes.
5.5.3 Locks of at least class III according to GOST 5089 . Locks must comply with the requirements of GOST 538 and GOST 5089 .
To improve the protective properties of door blocks, it is recommended to use multi-bolt locks with locking along the perimeter of the door block or locks with rods with additional locking in the upper and lower horizontal frame profiles.
To avoid clogging of the hole for the lower vertical bolt included in the bottom profile of the box, it is recommended to use deviators.
5.5.4 Depending on the purpose of the door blocks in the project documentation, as well as when placing orders, it is necessary to provide for the complete set of products with latches, door closers (closers), opening angle limiters (stops), eyes, chains, etc.
Once every two years
Reliability
Ergonomic Compliance
Reduced resistance heat transfer
Once every five years
Breathability
Soundproofing
* Test type I - acceptance tests during acceptance control; test type II - acceptance tests conducted by the quality service of the manufacturer; test type III - periodic tests carried out in independent test centers.
** Controlled nominal dimensions for test type II are set in the technological documentation.
6.5 Each batch of products undergoes control acceptance tests conducted by the quality service of the manufacturer. The list of controlled indicators and the frequency of control are given in the table.
To conduct tests, samples of door blocks are taken from a batch of products by random selection in the amount of 3% of the batch volume, but not less than 3 pcs. If there are less than 3 products in a batch, each product is subjected to control.
In the event of a negative test result for at least one indicator on at least one sample, a re-check of the quality of products is carried out on a double number of samples for the indicator that had a negative test result.
If a discrepancy between the indicator and the established requirements is detected again, at least on one sample, the control and subsequent batches of products are subjected to continuous control (sorting). With a positive result of continuous control, they return to the established procedure for acceptance tests.
6.6 Periodic tests according to the performance indicators specified in - are carried out when putting into production or when making changes to the design of products or their manufacturing technology, but at least once in the period specified in the table, as well as during product certification. In justified cases, it is allowed to combine periodic and certification tests.
Qualification tests of products are carried out for all indicators when putting products into production.
Tests are carried out in test centers accredited for the right to conduct them.
Tests to determine the reduced resistance to heat transfer, air permeability, sound insulation are subjected to structures designed to withstand these loads according to their field of application.
6.7 The consumer has the right to conduct a quality control check of products, while observing the sampling procedure and test methods specified in this standard.
When products are accepted by the consumer, a batch is considered to be the number of products shipped for a specific order, but not more than 90 pieces, drawn up with one quality document.
Limit deviations from the nominal dimensions of product elements, the difference in the lengths of the diagonals and other dimensions are determined using a metal measuring tape according to GOST 7502, calipers according to GOST 166, probes according to ND.
The maximum deviations from the straightness of the edges are determined by applying a calibration ruler in accordance with GOST 8026 or a building level with a flatness tolerance of at least the 9th degree of accuracy in accordance with GOST 9416 to the tested part and measuring the largest gap using feelers according to ND.
7.2.2 Limit deviations from the nominal dimensions of the gaps under the overlay are checked using a set of probes or a ruler in accordance with GOST 427.
7.2.3 The sag in the mating of adjacent parts lying in the same plane is determined with a probe as the distance from the edge of the ruler according to GOST 427, applied to the upper mating surface, to the lower surface.
7.2.4 Appearance, quality of welds, color and quality of finishing of products are evaluated visually by comparison with standard samples approved in the prescribed manner. Surface defects visible to the naked eye from a distance of 1.5 m in natural light of at least 300 lux are not allowed.
7.2.5 Adhesion (strength of adhesion of paint and varnish coatings to the metal surface) is determined by the method of lattice cuts according to GOST 15140 .
8 Packaging, transport and storage
8.1 Packaging of products must ensure their safety during storage, handling and transportation.
8.2 Devices or parts of devices that are not installed on the products must be packed in polyethylene film in accordance with GOST 10354 or in other packaging material that ensures their safety, tightly tied and delivered complete with products.
8.3 Opening webs of products before packaging and transportation must be closed on all locking devices.
8.4 Products are transported by all means of transport in accordance with the rules for the carriage of goods in force for this type of transport.
8.5 During storage and transportation of products, they must be protected from mechanical damage and exposure to precipitation.
8.6 When storing and transporting products, it is recommended to install gaskets made of elastic materials between products.
8.7 Products are stored in a vertical or horizontal position on wooden linings, pallets or in special containers in covered areas.
8.8 Warranty period of storage of products - 1 year from the date of shipment of products by the manufacturer.
9 Manufacturer's warranties
9.1 The manufacturer guarantees the compliance of products with the requirements of this standard, provided that the consumer complies with the rules for transportation, storage, installation, operation, as well as the scope established in the regulatory and project documentation.
9.2 Upon agreement with the consumer (customer), the manufacturer provides service, including emergency opening of doors in case of loss or breakage of keys, advice on the use and operation of door devices and locking mechanisms, and repair of products.
9.3 The warranty period for door blocks is set in the supply contract, but not less than three years from the date of shipment of the products by the manufacturer.
A -door block right opening; b - left opening door block; V - right opening door unit with horizontal and vertical leaf inserts
(reference)
An example of determining the strength class of a door unit
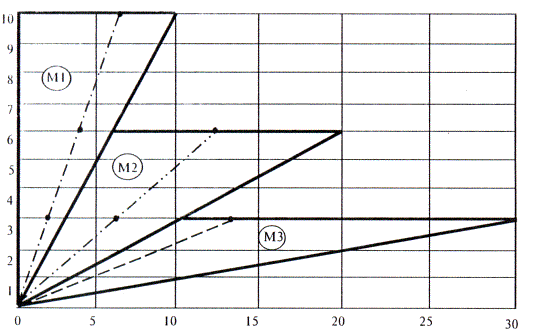
Figure D.1 -Deflection curve Δf, mm, web free angle from the applied load R, kN, when testing door blocks for resistance to static load acting perpendicular to the leaf plane in the area of the free corner
An example of filling out a door block passport
|
___________________________________________________ |
|
(name of manufacturer) |
|
__________________________________________________________________ |
|
(address, phone, fax of the manufacturer) |
|
Passport(quality document) |
|
a) design - single-floor, right-hand execution, with a threshold, opening inwards; |
|
b) overall dimensions - height 2300 mm, width 970 mm. |
|
Symbol DSN PPVn 3-2-3 M2 U 2300-900-60 GOST 31173-2003 |
|
Certificate of conformity ____________________________ |
|
(certificate number) |
|
Completeness |
|
a) type of finishing of the canvas - combined (milled MDF board; vinyl artificial leather); |
|
b) door hinges- two overhead bearing loops; |
|
c) locking devices - a lever lock and a lock with a cylinder mechanism; |
|
d) the number of contours of sealing gaskets - 2 circuits; |
|
e) additional information. The delivery set of the product includes: closer (closing regulator), door stop (opening limiter), instruction manual. |
|
Main technical characteristics confirmed by tests |
|
The reduced resistance to heat transfer is 0.65 m 2 · ° C / W. Air permeability at Δ P0 \u003d 100 Pa - 15 m 3 / (h m 2). Sound insulation - 22 dB. |
|
Reliability, opening - closing cycles - 500,000. Mechanical characteristics class - M 2. |
|
Warranty period - 3 years. |
|
Batch number - 89. |
|
Order number / position in the order - 17/9. |
|
Quality Control Receiver._________________ Date of manufacture "___" ____________200__. |
|
(signature) |
Appendix E
General requirements for the installation of products
E.1 Requirements for the installation of products are established in the design documentation for construction projects, taking into account the design options adopted in the project for the junction of products to walls, designed for given climatic and other loads.
E.2 Installation of products must be carried out by specialized construction companies or specially trained teams of the manufacturer. Completion of installation work must be confirmed by an acceptance certificate, which includes the manufacturer's warranty obligations.
E.3 At the request of the consumer (customer), the manufacturer (supplier) of products must provide him with standard instructions for the installation of door blocks, approved by the head of the manufacturer and containing:
drawings (diagrams) of standard mounting junctions;
list of materials used (taking into account their compatibility and temperature conditions applications);
the sequence of technological operations for the installation of door blocks.
E.4 In the design and execution of junction nodes, the following conditions must be met:
sealing of mounting gaps between products and slopes of openings of wall structures should be tight, tight around the entire perimeter of the door block, designed to withstand climatic loads from the outside and operating conditions inside the premises;
the design of the junction points of external products (including the location of the door block along the depth of the opening) should prevent the formation of cold bridges (thermal bridges) leading to the formation of condensate on internal surfaces doorways;
the operational characteristics of the structures of the junction points must meet the requirements established in the building codes.
The version of the mounting assembly of the internal door unit is shown in the figure

1 - box (frame) of the door block; 2 - polyurethane foam; 3 - outer seal; 4 - leaf of the door block; 5 - inner seal; 6 - decorative frame portal; 7 - casing; 8 - mounting anchor; 9 - mounting ear; 10 - wall
(reference)
Information about the developers of the standard
This standard has been developed by a working group of specialists consisting of:
Vlasova T.V., TsS ODT (head);
Mogutov A.V., NIISF RAASN;
Voronkova L.V., Federal State Unitary Enterprise TsPKTB Gosstroy of Russia;
Shvedov D.N., TsS ODT;
Savchenko I.F., TsS ODT;
Savenkov A.V., ANOO Academy "Security and Law";
Petrov E.V., Association "Derzhava";
G. Engblom, Abloy Oy, Bjerkboda plant, Finland;
Gavrilov V.I., CJSC NPVF "Class";
Naan G.G., LLC BIT "Soyuz";
Vlasov A.A., Metal Geometry LLC;
Teplyakov N.N., Voronin V.M., NPP Modul LLC;
Leibman A.A., Leibman G.A., Le-Grand LLC;
Fatykhov Kh.T., Olenev V.T., Guardian Company;
Hitkov V.Yu., Malovichko V.V., Sonex LLC;
Savic B . C., FGUP CNS;
Shvedov N.V., Gosstroy of Russia.
Keywords: door blocks, door leaf, frame, steel sheet
Plastic doors firmly entered our lives. You can’t even imagine the entrance to shops, offices, shopping centers from another material, PVC is widely used. The abbreviation PVC stands for Polyvinyl Chloride. This popular material is widely used for the production of doors and windows. Today, everyone appreciated the strength, tightness and durability plastic products, their elegance, as well as ease of care and maintenance.
Basic definitions
In the manufacture of the door structure, to give strength, the PVC profile is reinforced inside with aluminum liners. That is why such products are also called metal-plastic. The requirements for them are set out in GOST "Door blocks made of polyvinyl chloride profiles" (GOST 30970-2002). The sizes and a form of products are defined by the customer.
GOST of the Russian Federation was introduced on March 1, 2003. It defines the rules for the designation of PVC door blocks and their classification:
- by appointment;
- constructive decision;
- type of filling;
- profile designs;
- finishing.
The standard should be followed by manufacturers producing PVC plastic products. Buyers will also learn a lot of useful information from GOST, which will help not to make a mistake when choosing a product.
Door blocks have the following purpose:
- external, these include entrance street doors and vestibules;
- internal, subdivided into interior, balcony, bathroom and toilet.
By design, door blocks are divided into single-floor and double-floor. Single-field open to the right and left and are designated respectively (P, L). Double-sided are most often equipped with a shtulp closing system. In addition, blocks come with and without a threshold, with a transom on top or on the side.
The door leaf according to the type of filling can be:
- deaf (filled with insulation);
- glazed (a double-glazed window or sheet glass is installed);
- light (the bottom is made of canvas, and the top is glass);
- decorative.
The PVC profile of products differs in the number of internal chambers: two, three or more.
Profile finishing is divided into the following types:
- dyed in mass (white or colored);
- laminated;
- painted (varnish or paints).
Technical designations
The requirements defined in GOST apply to products whose area is not more than six square meters. In this case, the area of the opening canvas should not exceed 2.5 m2. Restrictions on the mass of the canvas are 80 kilograms.
When manufacturing products of a larger area or weight, additional calculations or strength tests must be performed.
When buying plastic doors, it is advisable to understand the designations given in the documentation. For example, let's decipher the designation DPVM GB L 2200-1500 GOST 30970-2002.
The first letters are deciphered as follows: DPV - internal PVC door block (or DPN - external). It is allowed to supplement with a fourth digit specifying the purpose of the door: M - interior. Through a space, the type of internal filling of the canvas is indicated: G - deaf. The sixth digit means: B - no threshold. The seventh letter L denotes a single-floor design solution indicating the direction of movement. The double door is designated Dv. The numbers 2200-1500 indicate the size of the door leaf: height and width.
The dimensions of the doorway of residential premises are determined by building codes and have the following values:
- height - from 2170 to 2419 mm;
- width - from 70 to 910 mm.
The opening for entering the apartment according to GOST must have a size of at least 910 mm.
The maximum dimensions of plastic sheets - height and width for specific brands are prescribed in the technical documentation (TU) for a specific product.
Operating requirements
For entrance outdoor, apartment and balcony products, the requirements for heat transfer, sound insulation, air permeability, opening cycles and durability must be met.
In GOST, the value of resistance to heat transfer is given depending on the thickness of the filling with three-layer panels. With a layer thickness of 16 to 24 mm, the resistance coefficient should be within the following limits: 0.8-1.2 m 2 C / W. Sound insulation should not exceed 26 dBA, and the air permeability of the structure should not exceed 35 m 2 / (h m 2).
The number of opening/closing cycles of entrance doors according to the requirements of GOST should not be less than 500,000.

Heat transfer is one of the main requirements for external plastic doors.
Service life of the main parts door structures PVC is classified as follows:
- profiles - 40 years;
- double-glazed windows - 20;
- seals - 10.
According to the degree of strength, PVC profiles are divided into classes A, B and C. In the manufacture of door structures, class A profiles are used, having a front wall thickness of 3 mm. The strength class is determined during testing.
If the width of the welded sheets exceeds 600 mm, then such a corner joint is reinforced with metal inserts. To increase resistance to intentional penetration, various options are allowed:
- installation of additional locks;
- glass up to 10 mm thick;
- anti-removable devices;
- reinforced loops.
The design of the porches
Two-field structures can be closed with an impost or a sash structure. An impost is a plastic partition separating a door or window, in which a groove for closing is mounted. Modern shtulpovy design allows you to open both halves of the door without creating obstacles and without disturbing the view.
The shtulpovy design is actual for offices, shops and entrance doors to the house. At the same time, one half can be fixed on the latch and open if necessary to transfer furniture or other bulky things. Old interior or balcony doors of the two flaps, they will perfectly replace the plastic ones with a shtulpa that swing wide open outward. In the case of a balcony design, this design allows for a more rational use of the area of the room.

Shtulpovy design is especially relevant for a balcony door
Gradually, the impost is becoming a thing of the past, giving way to a more rational design - the shtulp one. In addition to improving the appearance, saving material, increasing the luminous flux, the shulp system has increased burglar resistance. Two plastic sashes are connected by snapping and it is quite difficult to break them from the outside, unlike the impost construction. The locking mechanism can be attached to one leaf or two, and only a specialist can notice it.
Users also note good density fit of door leaves with a shtulpovy latch. This is especially true for the balcony door, as it allows you to keep warm in the apartment. Among the mechanisms of the shtulp design, a simple and economical bolt version stands out. Latches on the passive sash at the bottom and top, and on the active sash - a handle that activates the door opening system.
Features of PVC balcony doors
Traditionally, balcony doors are made in the same design as the window. Therefore, in the manufacture of a balcony structure, there are some peculiarities. The advantage of PVC products over other materials is:
- tight fit of the canvas to the frame and ease of opening / closing;
- resistance to temperature changes;
- air tightness and low heat transfer, so that the room does not leak heat through the balcony door;
- ease of care.

Plastic balcony doors should fit snugly against the frame and not let air through.
Plastic balcony doors are made from window profile as a whole, therefore, the same tilt-and-turn mechanisms are used as for windows. At the request of the customer, the product is equipped with a double-sided handle to prevent accidental snapping while on the balcony. Fittings (hinges, latches, etc.) are also used window.
Balcony doors are made with glass on the entire door leaf or with partial glazing, when the lower part is made deaf. Full glazing allows you to change the lighting of the room and add zest to the interior. Options with or without a threshold are also allowed.
If the balcony is glazed, then it is enough to install a single-chamber double-glazed window on the door. WITH open balcony to save heat, at least a 3-chamber profile and a double-glazed window are used.
The size of the product is determined by the height and width of the opening. Standard size is: height - at least 190 cm, width - 60 cm. If the size of the balcony opening exceeds 90 cm, a shtulp closing system is used. If it is necessary to reduce the size of the opened sash, the second part is made deaf or closed with latches. Given the variety of sizes and shapes of windows, the manufacture of balcony blocks is made according to individual projects.
In the manufacture of a balcony door, it is necessary to be guided by GOST 30970-2002 "Door blocks made of polyvinyl chloride profiles."
To maintain the interior of the room, plastic balcony doors are made in different options execution: white or colored laminated, leaving room for the creativity of the owners.
Specifications and GOST for PVC doors
To date, there is no person who has not heard of PVC doors, also called metal-plastic or simply plastic. By using them in Everyday life How often have we wondered what it is?
Such doors are usually made of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) material reinforced inside aluminum structures. Hence the name - metal-plastic. PVC is a hard-to-ignite and self-extinguishing material, not susceptible to atmospheric influences, as well as to the destructive action of alkalis and acids, and is not subject to rapid wear. It is these characteristics that make it possible to use it for the manufacture of door frames. Also, a PVC door is much cheaper and often more beautiful, as indicated by customer reviews.

Any person who buys a PVC door should know that the opportunity to choose a really high-quality product is regulated by law. Since 2002, the State Standard for metal-plastic doors has been used. It is called "Door blocks made of PVC profiles" (GOST 30970-2002).
This standard describes the main types of metal-plastic doors and their technical characteristics that require production. GOST obliges manufacturers to adhere to all the quality standards described in it. Therefore, when purchasing a metal-plastic door, in order not to blindly trust the seller, it is important to understand the basic concepts of GOST.
Typology of PVC doors according to GOST
Corresponding to GOST 30970–2002, metal-plastic doors are divided into:
- Regarding the purpose, the door can be external, and internal. Inner door, can be an interior door, an entrance door to an apartment or a bathroom;
- Regarding the type of door frame filling:
- glazed PVC door, in the frame of which a double-glazed window or transparent glass of any kind is inserted;
- a deaf door, the door leaf of which is opaque. It can also be: light (when the lower part of the door is not transparent, and the upper part allows light to pass through) and decorative (when the PVC door leaf is equipped with an architectural pattern);
- Regarding its design, a metal-plastic door can be:
- with one canvas (right or left) and with two canvases (the same or different widths);
- with a fixed sash or with one that opens;
- with or without a threshold, with or without a frame box;
- regarding the type of PVC profile.

Here the classification occurs according to the number of chambers of the profile system from which the door is made. Profiles come with two three or more cameras;
- With regard to the finish of the profile, the PVC door can be white or in a different color, covered with a laminating film or with a co-extruded face covering.
Technical requirements for PVC doors according to GOST 30970–2002
The state standard rather strictly regulates the parameters that the production of plastic doors can afford - these are the dimensions, the filling of the leaf, the permissible deviations in the manufacture. Accordingly, the requirements are put forward in relation to fittings. Also in this document are prescribed measures for quality control of products, standards for their packaging, transportation and storage.
Characteristics of the operation of a plastic door
In order for the door you bought to satisfy your needs and maintain the necessary microclimate in the house, when choosing, you need to pay attention to its main characteristics:
- Heat transfer resistance may depend on thickness insulation material, but should not go beyond 0.8-1.2 m²xS / W.
- Air permeability is not more than 3.5 m³/(chxm2).
- Isolation from sound waves not less than 26 dBA
- The state standard also establishes that the number of years of use for a PVC profile must be at least 40, for a double-glazed window - at least 20, for a sealant - at least 10. The number of opening and closing during this period can be at least 500,000 times.

Strength groups of metal-plastic doors
When buying, the strength group is also an important indicator for the door. There are only three of them: A, B, C. The most durable, according to this GOST classification, are the doors of group A. You can also find out about this by reading customer reviews.
What deviations can be considered a defect in the production of PVC doors
Production in violation of the requirements of the State Standard occurs in cases where:
- There is a difference in the dimensions of the finished product and the dimensions that are indicated in the project documentation. The difference should not be more than 2mm and less than 1mm. The difference in diagonal length for PVC doors should not exceed 2 mm for a 1.5 m2 door leaf and 3 mm for larger doors.
- Scratches, chips and other deformations are found on the door leaf, as well as a difference in color or gloss that are visible to the naked eye.
- The door opens and closes with effort and force.
- There are deviations of the technical characteristics from the one stated in the documentation.
- Deviations from GOST requirements during installation.

When buying a PVC door, do not forget that you have the right to demand compliance with the requirements of the State Standard from any company operating in the Russian Federation.

Building company. I am collecting commercial offers for doors made of PVC profile for the school. I'll send you the spec.
Specifications, GOST for the door: what does it mean?
Everyone knows that the theater begins with a hanger. One cannot argue with the classic, but the first thing that a human eye stumbles upon is doors. Their appearance, durability and quality best of all characterize both the room you are going to enter and the owner himself. In this article, we will talk about what types of products exist, what is GOST of metal-plastic doors and why it was created

Reference: GOST is a category of accepted standards, which are presented as normative non-legal acts. Become mandatory after registration with the Ministry of Justice. This is an important precept of production standards, designed to increase the level of security of citizens and interact with maximum efficiency various industries. And, therefore, under standard metal-plastic doors, the manufacturer will be able to easily find the necessary fittings.
What do the numbers and letters mean in GOST
The manufacture of products from PVC profiles is regulated by GOST 30970 2002. Doors made in accordance with the requirements of this GOST are made in compliance with all technical requirements. The marking contains letters and numbers, the meaning of which carries important information set out below.
The combination of DPV means what type of product is presented: the letter “B” indicates that the block is internal, and the letter “H” (DPN) indicates external metal-plastic doors.
- C - the block is used to equip sanitary facilities.
- T - in vestibules, corridors.
- M - between rooms.
The following symbols indicate how the canvas is filled.
- Glazed doors are marked with the letter O.
- Deaf plastic door - G.
- Decorative canvas, or clarified - S.
What design of doors you see in front of you is clear from these symbols.
- P - a product with a threshold.
- B - design without a threshold.
- F - indicates the presence of a transom.
- K - means that the box is closed.
What direction a single-leaf door has when opening will become clear when reading the marking “L” or “Pr”. And if the product is double-sided, then in the same place you will see the letters "Dv". But the dimensions in millimeters will be indicated by subsequent numbers. PVC windows will be marked in accordance with GOST in the same way.
For ease of perception, all this fits into the framework of a certain classification.
- Appointment of door blocks.
- Designs and solution.
- Type of filling.
- Execution of profile systems.
- Finish type.
The last 2 points provide for the number of cameras in the profile system of the block and painting or laminating with a film.
PVC, metal-plastic, plastic - what's the difference?
We are talking about the same product. The full name of doors or windows will sound like this: reinforced or metal-reinforced plastic (made of polyvinyl chloride) door blocks. Therefore, GOST of a metal-plastic door, GOST of plastic doors and GOST of polyvinyl chloride doors is expressed by a single adopted provision.
Special technical and operational characteristics and requirements
Door and window blocks must perform the main functions, which are expressed by the following operating characteristics:
- strength group from the strongest "A" to the weakest "B";
- the durability of the profile is 40 years, the double-glazed window is 20, and the seal is 10 years;
- low level of heat transfer with an indicator from 0.8 to 1.2 m²xS / W;
- sound insulation should not fall below 26 dBA;
- air permeability should not exceed 3.5 m³ (hxm²);
GOST on PVC doors also meets the basic technical requirements:
- the profile must be connected firmly and tightly;
- products are manufactured with obligatory observance and in accordance with technological documentation;
- in order to remove moisture from the outside of the blocks, special holes must be placed;
- so that the color profile does not overheat, holes also come out through the outer sides of the chamber;
- all component parts from which the blocks are assembled must be manufactured in accordance with the GOST established for them;
- the weight of canvases not exceeding 6m² with an area of elements that open 2.5m² cannot exceed 80 kg;
- the use of blocks must be safe, which is necessarily reflected in the project documentation and is confirmed by the presence of an appropriate certificate;
- compliance with existing fire regulations is required.
The technical characteristics of the door GOST 30970 2002 were established in 2002 with minor changes in 2014. PVC windows GOST 30970 2002 must also meet specially developed standards corresponding to GOST.
Features of balcony doors
GOST requirements for PVC balcony doors are somewhat different. They are detailed in GOST 30673 - 99.
- In these blocks, various channels and valves are used to improve the humidity regime of an apartment or house.
- To enhance sound insulation, special valves are mounted in products that absorb noise.
- Balcony doors withstand increased operational loads, such as strong winds, provided for by established standards. Increased attention is paid to resistance to the effects of static loads.
- In the technical designations of the block passport, you can see the letter M, which is added when using the frost-resistant version of the product.
- The design of balcony blocks is installed with increased attention to fire safety.
- To increase the heat-shielding properties, balcony double-glazed windows are filled with a special gas.
- GOST of plastic balcony doors provides for strengthening the profile of products with liners coated with an anti-corrosion compound.
GOST 30970-2002 for plastic entrance and interior doors
The spread of technology for the manufacture of PVC door blocks has led to the need to develop generally accepted standards for these products. Therefore, in 2002, an interstate standard was published (GOST 30970-2002), regulating the requirements for door blocks made of PVC profile. This regulatory document regulates the standards by which hinged plastic doors are produced. The requirements of GOST 30970-2002 do not apply to plastic models special purpose, including balcony doors.
The development and implementation of state standards is the only way to oblige manufacturers to produce products that meet certain requirements. In the absence of a generally accepted GOST, manufacturers work according to specifications developed independently. As a result, similar products manufactured at different enterprises may have various properties and vary greatly in quality.
It is very important to introduce GOST for products that are used in the construction industry. After all, the reliability of the constructed structures, and, consequently, the safety of people, depends on the properties and qualities of the manufactured products.
Current regulatory documents
The beginning of mass production of plastic doors and windows took place at the end of the last century. In 1999, GOST 30673-99 was adopted, which regulated the requirements for PVC profiles, from which window and door blocks were assembled. The state standard made it possible to put things in order in the production of plastic products, which were previously produced according to specifications developed by each company independently. 
To date, according to the requirements of GOST 30674-99 and GOST 232166-99, balcony doors are made of PVC.
For external door plastic blocks and interior doors from PVC, GOST 30970-2002 is used. This regulatory document describes the technology for the manufacture of plastic doors, the standard value of the parameters and possible deviations from the standards.
Features of the production of plastic doors
Plastic balcony doors are made using the same technology as PVC profile windows. In fact, a balcony door is just a large plastic window with hinged or (less commonly) pivoting sashes. 
Different requirements are imposed on interior and entrance doors, therefore, in 2002, a regulatory document was adopted that regulates the production of these products. Interior and especially facade plastic doors should be more burglar-resistant and reliable than models installed on a balcony block.
Specifications
Basic requirements for plastic doors, regulated by GOST:
- Heat transfer resistance - 0.8-1.2 m² * C / W (depending on the type of insulation).
- Sound insulation - not less than 26 dB;
- Air permeability - no more than 3.5 m³ / h * m²
What is considered a marriage of a plastic door?
A serious violation of the requirements of GOST or, in other words, a marriage of a plastic door is considered:
- Significant deviations of dimensions from those stated in the documentation. The permissible deviation in dimensions is -1 mm / +0.2 mm.
Advice! There is a limited tolerance for the difference in measurements of the diagonal length of the door leaf. For doors with a total area of up to 1.5 m², this tolerance is 2 mm, if plastic doors have an area of \u200b\u200bmore than 1.5 m², then the measurement mismatch tolerance is 3 mm.
- A marriage of a plastic door is the presence of various surface defects - chips, dents, scratches. Unacceptable surface defects include the difference in the degree of gloss, shade, visible to the naked eye.

- High-quality doors should be easy to close and lock if they are equipped with latches or locks. According to the requirements of GOST, when closing the door, with the required deformation of the seals, the force should not exceed 120N.
- The presence of deviations of real specifications doors from the values stated in the documents is considered a marriage.
Advice! GOST regulates not only the manufacturing standards and characteristics of plastic doors, but also the rules for their installation. Plastic doors are mounted in accordance with the requirements of GOST 30971.
Varieties of plastic doors
In modern construction, a wide variety of doors made of plastic are used.
Classification by purpose
Plastic doors by appointment can be:
- Facade or outdoor;
- Internal.
The latter type of doors is subdivided into entrance, installed in entrances or common corridors, interior doors, balcony doors, doors for bathrooms and saunas.
By filling type
By given parameter There are the following types of plastic doors: 
- Deaf. These are doors having a canvas filled with sandwich panels or other opaque material.
- Glazed. Models with a glass insert, it can be a multi-layer double-glazed window, patterned or tinted glass.
By type of construction
Plastic doors, like conventional swing models, can be:
- Single and double sided.
Advice! Double-leaf models can have sashes of both equal and different widths. In addition, two-leaf models are distinguished, in which both wings are movable, or those in which one of the wings is fixed in a fixed position.
In addition, doors can be equipped with a threshold or have a frame structure in which the role of the threshold is assigned to the bottom bar of the frame.
By type of finish
On this basis, the following types of plastic doors are distinguished: 
- Completely painted in white color;
- Fully dyed in any other shade than white;
- Laminated, i.e. pasted over decorative film. The film can imitate various surfaces, most often it is an imitation of the structure of wood or stone.
So, plastic doors are produced according to the requirements of GOST, the main requirements for products are formulated in the regulatory document.
Characteristics of plastic doors "VEKA"
System of metal-plastic doors "VEKA"
Technical features of plastic doors "VEKA"
Special strong steel reinforcements with integrated corner connectors ensure high stability of VEKA door structures.
The geometry of the systems ensures the use of the widest range of door fillings - and significantly expands the range of design solutions.
Thresholds with thermal breaks guarantee excellent thermal insulation.
Door sill extensions provide high static and energy-saving performance of finished door structures.
Doors "VEKA" have modern design thanks to the elegance of the design and glazing beads. Plastic doors "VEKA" can be supplied both in white and in one-sided or two-sided color version.
Doors of the VEKA system are made of high-quality plastic. Environmentally friendly and have a rich glossy white color.
Advantages of the door profile "VEKA"
The door structure of a hinged door consists of a box, which is fixed in the wall opening and a blank or glazed leaf, hung on the box. A box with a hanging leaf forms a door unit.
Entrance house doors. Doors leading from the room to the street protect the interior from various atmospheric influences; they themselves must be protected from hacking and have an attractive appearance. It is most rational to place external doors on the side opposite to the direction of the prevailing winds; thus, hit of jets of slanting rain on a door will be minimized. In a different arrangement, it will often be necessary to restore the color and repair the outer door. In addition, in this case, in the lower part of the door block, it is necessary to provide special measures against the leakage of rainwater during strong winds or protect the entrance doors with the help of canopies, visors or vestibules. Tambours are rooms that serve as a buffer zone between outdoor and indoor air. Thanks to the tambour in winter cold air cannot directly penetrate into the apartment, and warm air cannot go outside. Tambours, therefore, perform a heat-shielding function. They are also often a place where dirt and moisture remain and do not penetrate further into the house or apartment.
It is often necessary to provide high heat-shielding properties interior spaces, in this case, the entrance doors are thermally insulated, and to increase the soundproofing properties, the door leaf is backfilled with heavy bulk materials such as sand or lead shot.
Double-skinned doors consist of two layers sewn together with nails or glued boards. Double skin can also be at the paneled door. The quarters are formed by a recess in the double skin.
Paneled doors (doors of the strapping structure) consist of a strapping and a panel. Panels made of glass or wood can be installed in the grooves of the strapping, be floating or closed with a glazing bead.
The strapping elements are connected into a spike and a groove, wedged and glued together. With a strapping thickness of more than 50 mm, the corners are connected with a double spike. There is also a connection under acute angle into a small spike.
The doorway is blocked from above by a jumper, which transfers the load from the overlying structures to the piers. The size of the doorway should be slightly larger than the door frame. It is desirable that between the box and the wall there is a gap of at least 2 cm wide, which can be used for laying heat-insulating material.
The door frame is a frame made of bars with folds, which are fixed with steel plates or with expansion dowels. For doors with heavy leafs, anchors embedded in the masonry should be used.
For a door frame with a threshold in the floor, two embedded parts are used. If the width of the door leaf exceeds 1250 mm, the frame is additionally fixed in the middle of the upper horizontal bar. On the sides it is fastened with dowels, and at the top and in the threshold - with screws. Thin wooden planks are placed at the attachment points so that there are no voids between the wall and the box and it stands straight. Countersinks are made under the heads of nails and screws (recesses made with a countersink - a drill-spear, a triangular spatula - for sinking the heads of nails, screws, screws). Then these places are puttied.
Hanging the door leaf and checking the accuracy of the fit (if the leaf touches the lower bars of the box when opening, it is lifted or planed from below).
Checking the tightness of the door porch and the operation of the lock. Fastening the side of the box where the lock is embedded with two nails and a secondary check of the accuracy of fitting the canvas to the box.
Doors are usually attached at three points in height to the vertical bars of the box. Attachment points are located as far as possible at a height convenient for work. for doors standard height the extreme attachment points are usually removed about 30 cm from the top bar of the box and 25 cm from the threshold.
Boxes are aligned and secured with wedges; then they are connected to the embedded part installed in the masonry. If steel plates are used, then first they are attached to the box, and after installing the box in the opening, the other end of the plates is attached to the wall with nails or dowels. In two or three places along the height of the box, small holes are arranged through which they are injected into the gap cement mortar. To prevent the vertical bars of the box from bending inside the opening when the solution is injected and hardened, they are temporarily unfastened with a special spacer or an ordinary board.
Cloths of external entrance doors are hung in boxes on hinges with non-removable rods, on spring hinges that allow door leaves to be opened in both directions, or mounted on thrust bearings.
Apartment doors, that is, doors separating the premises of apartments from staircase or vestibule, must be burglar-proof, soundproof and keep warm inside the apartment. The sound insulation capacity must be certified by a test certificate from an authoritative government agency. The degree of sound insulation of the door is largely determined by its weight, as well as the properties of the material filling the interior space.





























