Bitumen roofing soft tiles easy to use, durable and aesthetically pleasing. Its big advantage is that it is quite possible self-installation. The technology is not the most complicated, the weight of the fragment is small, it is attached to an adhesive base, and is additionally fixed with roofing nails. So you can do the installation of soft tiles with your own hands even alone.
Roofing pie for soft tiles
The attic under the roof can be warm or cold, depending on this the composition of the roofing cake changes. But its part from the rafters and above always remains unchanged:
- waterproofing is installed along the rafters;
- on it - bars with a thickness of at least 30 mm;
- solid flooring.
Let’s look at these materials in more detail - what and how to make them from, what features each of them has.
Waterproofing
Waterproofing membranes come in one, two and three layers. Single-layer membranes are the simplest and cheapest, they perform only a double task - they do not allow moisture to pass into the room and release vapors to the outside. So in a simple way not only is the attic protected from the penetration of condensation or precipitation that suddenly seeps in, but also excess moisture that accompanies human activity is removed from the air. Single-layer membranes are poorly represented on the market. They are practically produced by one company - Tyvek.

Two- and three-layer membranes are more durable. In addition to the waterproofing layer, they also have a layer that gives greater tensile strength. The third layer, if there is one, is the adsorbent layer. That is, even if a drop of condensate forms on the surface of the membrane, this layer absorbs it, preventing it from spilling onto other materials. With sufficient ventilation, moisture from this layer gradually evaporates and is carried away by air currents.
Three-layer membranes (for example, EUROTOP N35, RANKKA, YUTAKON) are desirable if your attic is insulated and mineral wool is used as insulation. It is afraid of getting wet and when humidity increases by 10%, it loses half of its thermal insulation properties.
If there is a cold attic under soft tiles, it is advisable to use a two-layer waterproofing membrane. In terms of strength, it is much better than single-layer ones, and the price is only slightly more expensive.
Lathing
Sheathing strips are placed on top of the waterproofing film, parallel to the overhang. They are necessary to create a ventilation gap. It will maintain normal humidity of roofing materials.

The sheathing is made from boards conifers(mainly pine trees). The thickness of the boards is at least 30 mm. This is the minimum gap that will ensure normal air movement in the under-roof space. Before laying, the wood must be treated with an impregnation that protects against pests and fungi; after this layer has dried, it is also treated with fire retardants, which reduce the flammability of the wood.
The minimum length of the board for sheathing is at least two spans of rafters. They are attached and connected above the rafter legs. You cannot connect them anywhere else.
Flooring
The flooring for soft tiles is made continuous. The materials are selected based on the fact that nails must be driven into it, therefore they are usually used:
- OSB 3;
- moisture-resistant plywood;
- tongue and groove boards of the same thickness (25 mm) with a moisture content of no more than 20%.
When laying flooring under soft tiles, gaps must be left between the elements to compensate for temperature expansion. When using plywood or OSB, the gap is 3 mm, between edged boards 1-5 mm. Sheet material They are fastened with seams staggered, that is, so that the joints are not continuous. The OSB is secured using self-tapping screws or rough nails.

When using boards as flooring, you must ensure that the annual rings of the wood are directed downward. If they are positioned in the opposite direction, they will bend in an arc, the soft tiles will lift, and the tightness of the coating may be compromised. There is one more trick that will keep the wooden flooring level even if the moisture content of the boards is above 20%. When laying, the ends of the boards are additionally secured with two nails or self-tapping screws driven close to the edge. This additional fastener will prevent the boards from bending when drying.
The choice of thickness of material for flooring under soft tiles depends on the pitch of the sheathing. The larger the pitch, the thicker the flooring required. The best option- frequent step and thin plates. In this case, a light but rigid base is obtained.

Another point concerns the installation of flooring under soft tiles around the chimney pipe. For a brick pipe whose width is more than 50 cm, a groove is made behind it (pictured). This design, reminiscent of a mini-roof. It separates the rain streams, they roll down the sides of the pipe without flowing into the under-roof space.

After installing the flooring, its geometry is checked. The length and width of the slope at the top and bottom, the height of the slope on both sides are measured, and the diagonals are measured. And the last check is plane tracking - the entire slope must lie entirely in one plane.
Soft tile roofing technology
When purchasing, you will most likely be provided with instructions in which the installation of soft tiles will be described step by step and in detail, indicating all the exact dimensions that this particular manufacturer requires. These recommendations should be followed. However, it is worth getting acquainted with the order of work and their volumes in advance - in order to understand the intricacies of installation and the required amount of materials.
Let’s say right away that you need to handle soft tiles carefully when laying them - they don’t like being bent. Therefore, try not to bend or wrinkle the shingles unnecessarily (this is one fragment consisting of a visible and mounting part).
Overhang reinforcement
The drip bar is installed first. This is an L-shaped sheet of metal coated with paint or a polymer composition. Polymer coating is more expensive, but also more reliable. The color is selected close to the color bitumen shingles.

The drip strip is installed along the roof overhangs
The purpose of the drip strip is to protect the sheathing, rafter sections and flooring from moisture. One edge of the drip is placed on the flooring, the other covers the overhang. It is fastened with galvanized (stainless steel) nails, which are driven in in a checkerboard pattern (one closer to the fold, the second almost at the edge). The fastener installation step is 20-25 cm.

The drip strip is sold in two-meter pieces. Having laid the first element, the second is fastened with an overlap of at least 3 cm. If desired, the gap can be closed: coat the joint with bitumen mastic and fill it with sealant. At the same stage, hooks are installed, or at least nailed, which will hold the gutters.
Laying a waterproofing carpet
Regardless of the angle of the roof, a waterproofing underlay must be laid in and along the slope. It is sold in meter-wide rolls. An adhesive composition is applied to the bottom side, covered with a protective film or paper. Before laying, the paper is removed and the valley carpet is glued to the flooring.

Installation of a waterproofing carpet begins with laying it in the valley. Roll out the material to a meter width, distributing 50 cm on both sides of the bend. Here it is advisable to avoid joints, but, if necessary, the overlap of the two canvases should be at least 15 cm. Laying proceeds from bottom to top, the junction is additionally coated with bitumen mastic, the material is pressed well.

Next, the waterproofing carpet under the flexible tiles is laid along the eaves overhang. Minimum width carpet on a cornice overhang - the size of the overhang itself, plus 60 cm. The lower edge is located on top of the drip edge and can bend down a few centimeters. First, the carpet is rolled out, trimmed if necessary, then the protective film is removed from the back and glued to the backing. Additionally, they are fixed along the edges with stainless steel or galvanized nails with a large flat head (step 20-25 cm).

At the horizontal joints, the overlap of the two sheets is at least 10 cm, in the vertical direction - at least 15 cm. All joints are additionally coated with bitumen mastic, and the material is crimped.
Underlay carpet
Underlay carpet, like waterproofing carpet, is sold in meter-wide rolls, the back side is covered with an adhesive composition. The installation method depends on the roof slope and the profile of the selected bitumen shingles.

When using bitumen shingles with cuts (type Jazz, Trio, Beaver Tail), regardless of the slope, the underlayment is spread over the entire surface of the roof.

Installation of underlayment often requires trimming. This is done using a sharply sharpened knife. To avoid damaging the material below when cutting, lay down a piece of plywood or OSB.
Front (end) strip
Pediment strips are mounted on the side sections of the overhangs. These are strips of metal bent in the shape of the letter “L”, along the bend line of which there is a small protrusion. They protect the laid roofing materials from wind loads and moisture. The gable strip is laid on the flooring on top of the underlay or waterproofing carpet, fixed with nails (stainless steel or galvanized) in a checkerboard pattern with a pitch of 15 cm.

These planks also come in 2 m pieces and are laid with an overlap of at least 3 cm.
Marking the slope
To make the installation of soft tiles simple, markings in the form of a grid are applied to the underlayment or flooring. This is done using a paint cord. Lines along the eaves are drawn at a distance equal to 5 rows of tiles, in the vertical - every meter (the length of one shingle flexible tiles). This marking makes installation easier - the edges are aligned using it, and it’s easier to track distances.

Valley carpet
More valley material is laid on top of the already laid waterproofing carpet. It is slightly wider, serves as an additional guarantee of no leaks. Without removing the protective film from the bottom side, it is laid, trimmed at the bottom in the overhang area, and the boundaries are marked. Stepping back from the 4-5 cm mark, a special mastic with increased fixation, Fixer, is applied. It is applied from a syringe, with a roller, then rubbed into a strip about 10 cm wide with a spatula.

The valley carpet is laid out on the mastic, the folds are smoothed out, the edges are pressed. Stepping back from the edge by 3 cm, it is fixed with nails in increments of 20 cm.
Connection to a brick pipe
To bypass pipes and ventilation outlets, cut-outs are made from valley carpet or galvanized metal painted in the appropriate color. The surface of the pipe is plastered, treated with a primer.
When using a valley carpet, a pattern is made so that the material extends onto the pipe by at least 30 cm, leaving at least 20 cm on the roof.

The pattern is smeared with bitumen mastic, placed in place. the front part is installed first, then the right and left.

Part of the side elements is wrapped on the front part. Back wall installed last. Its parts extend to the sides.
At correct installation on the flooring around the pipe there is a platform completely covered with a valley carpet. Before laying the tiles in this place, the surface is coated with bitumen mastic.

The tiles extend onto the laid carpet on three sides, not reaching the walls of the pipe 8 cm.

The upper part of the junction is sealed using a metal strip, which is attached to dowels.

All gaps are filled with heat-resistant sealant.

Round pipe output
There are special passage devices for the passage of ventilation pipes. They are positioned so that the lower edge of the element extends onto the tiles by at least 2 cm.

Having attached the passage element to the roof, trace its internal hole. Along the applied contour, a hole is cut out in the substrate into which a round pipe is inserted.
The back part of the skirt of the passage element is coated with bitumen mastic, adjusted to the desired position, and additionally secured around the perimeter with nails. When installing soft tiles, the penetration skirt is coated with mastic.

The shingles are cut as close as possible to the protrusion of the penetration, the gap is then filled with mastic, which is covered with a special coating that protects against ultraviolet radiation.
Start strip
The installation of soft tiles begins with the laying of the starting strip. Usually it is a ridge-cornice tile or an ordinary one with cut petals. The first element is laid on one of the edges of the slope, with its edge touching the gable strip. The lower edge of the starting strip is placed on the dropper, 1.5 cm away from its fold.

Removed from the back before installation. protective film, the shingle is leveled and laid. Each section of bitumen shingles is fastened with four nails - in the corners of each fragment, 2-3 cm away from the edge or perforation line.

If a cut of ordinary tiles is used as a starting strip, some of it will lack adhesive. In these places, the substrate is smeared with bituminous mastic.
Installation of soft ordinary tiles
There are flexible tiles with an applied adhesive mass, protected by a film, and there is a composition that does not require a protective film, although it also fixes the elements well on the roof. When using the first type of material, the film is removed immediately before installation.

Before laying bitumen shingles on the roof, open several packs - 5-6 pieces. Laying is carried out from all packs at the same time, taking one shingle from each one in turn. Otherwise, there will be obvious spots on the roof that differ in color.
The first shingle is laid so that its edge does not reach the edge of the starting strip by 1 cm. In addition adhesive composition, the tiles are also secured with roofing nails. The amount of fasteners depends on the angle of the slope:

When installing soft tiles, it is important to drive the nails in correctly. The caps should press against the shingles but not break through the surface.
Valley design
Using a painter's cord, mark a zone in the valley into which nails cannot be driven - this is 30 cm from the middle of the valley. Then mark the boundaries of the gutter. They can be from 5 to 15 cm in both directions.

The upper corner, which is turned towards the valley, is trimmed
When laying ordinary tiles, the nails are driven as close as possible to the line beyond which nails cannot be driven, and the shingles are trimmed to the floor of the gutter laying line. To prevent water from flowing under the material, the upper corner of the tile is cut diagonally, cutting off about 4-5 cm. The loose edge of the tile is smeared with bitumen mastic and fixed with nails.

Pediment decoration
On the sides of the slope, the tiles are cut so that 1 cm remains before the edge (protrusion) of the end strip. The upper corner of the shingle is cut in the same way as in the valley - an oblique piece of 4-5 cm. The edge of the tile is coated with mastic. A strip of mastic is at least 10 cm. Then it is fixed with nails, like the rest of the elements.

If the flooring in the area of the ridge is made continuous, a hole is cut along the ridge, which should not reach the end of the rib 30 cm. Bituminous shingles are laid up to the beginning of the hole, after which a special ridge profile with ventilation holes is installed.

It is fixed with long roofing nails. Several elements can be used on a long ridge; they are connected end-to-end. The installed metal ridge is covered with ridge tiles. The protective film is removed from it, then the fragment is fixed with four nails (two on each side). The installation of soft tiles on the ridge goes towards the prevailing winds, one fragment overlaps the other by 3-5 cm.

Ridge tiles are ridge-eaves divided into three parts. There is a perforation on it, and the fragment is torn off along it (first bend it, press the fold, then tear it off).
The same elements can be cut from ordinary tiles. It is divided into three parts, without paying attention to the drawing. The corners of the resulting tiles are cut off - about 2-3 cm on each side. The middle of the fragment is heated with a hair dryer on both sides, placed in the middle on a block and, gently pressing, bent.
Ribs and bends
The ribs are covered with ridge tiles. A line is drawn along the bend at the required distance with a paint cord. The edge of the tile is aligned along it. The laying of flexible tiles on the edge goes from bottom to top, each fragment is glued, then, retreating 2 cm from the top edge, it is fixed with nails - two on each side. The next fragment extends 3-5 cm onto the laid one.

Roofing work, when the technology of laying soft tiles is used, requires the sequential performance of several tasks.
The materials used for work, including bitumen shingles, must comply with current standards and regulations.
Before performing roof installation work, it is necessary to prepare the surface on which the roofing material will then be attached. This can be either a solid surface or made in the form of a lath. A variety of materials can be used for such purposes. Wood is most often used.
To create a continuous flooring on which flexible tiles will be mounted, you can use moisture-resistant plywood, moisture-resistant particle board, tongue-and-groove or edged boards. When creating such a surface, it is necessary to leave a gap of three millimeters between separate elements to compensate for the thermal expansion of parts when the temperature changes. Plywood along the edges must be fastened with self-tapping screws or brushed nails.
In order to ensure long service wooden elements structures, they must be treated with antipyrines and antiseptics.

Both wind load and static load from fallen snow have a serious impact on roof elements, including soft tiles. When designing a roof, it is necessary to take into account its height, which should be determined depending on the strength and direction of the prevailing winds and the amount of snow falling. Based on this data, you need to use rafters of the required thickness and with the correct spacing. This and also right choice The thickness of the material forming the surface for laying the roof will allow the roof to withstand the resulting loads. You can be guided by the data given in the table below.
Of great importance for the long-term operation of the roof, including when the technology of laying soft tiles is used, is ensuring temperature regime. This is especially important when under the roof is located residential attic. Such purposes are ventilation and ventilation of the roof. This avoids the appearance excess moisture and mold growth on roof elements. Natural ventilation is formed thanks to prudently built-in elements:
- hole for air intake;
- channels or vents for its circulation;
- exhaust holes.

Often, the project of the house provides for the siding of the overhangs of the cornice with siding. In this case, it is necessary to additionally install ventilation grilles or so-called soffit strips. They provide air to the vents. If the cladding is done with clapboard, then ventilation can be provided in accordance with the figure below.
The size of the air circulation channels is determined by the slope of the roof slopes. At an angle of inclination greater than 20 degrees, the vents must have a height of at least five centimeters. At an angle of inclination less than 20 degrees, this height should be eight centimeters.
Exhaust elements can be made in the upper part of the roof as follows:
- grilles on the exhaust openings on the side parts of the roof;
- ridge aerator;
- hood with access to the roof.
Installation of the lining layer

This is carried out to eliminate possible roof leaks.
According to current standards, if the roof slope is more than eighteen degrees (1:3), an additional roll hydro insulating material located along the end and eaves edges of the roof, considered to be the most likely places for moisture penetration, to a width of at least 40.0 cm from the edge. It would be best to bring this material to the surface of the facade. The roof ridge is also additionally covered with insulation of at least 25.0 cm on each side.
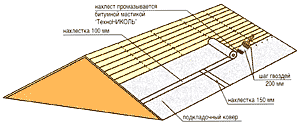
If the roof slope is from twelve to eighteen degrees, an additional layer under soft tiles is laid over the entire surface of the roof slope. This operation is performed from bottom to top, overlapping between layers. The rolled material is fastened with special galvanized nails with an enlarged head every 20.0 cm. The joints are additionally treated with bitumen mastic.
Before carrying out work on installing the base, if this is provided for in the project, it is necessary to attach hooks to the overhangs of the rafters for installing a suspended drainage system.
Laying end, cornice, parts and valleys
The roof overhangs must be reinforced with metal end and eaves strips on top of the lining layer. The planks are laid overlapping; for their fastening, roofing nails are used in increments of no more than 12 cm. Flexible self-adhesive tiles are laid end-to-end along the eaves on top of the metal plank.

Installation of tiles begins with the removal of the protective film, each tile is fastened with nails to the base. A special valley carpet is laid in the valleys. All rolled materials are additionally secured to the base with nails at the edges and treated with bitumen mastic.
Laying flexible tiles
If a dormer window is provided, then when installing flexible tiles, it is necessary to mark the slope to ensure correct joining of the shingles after the window.
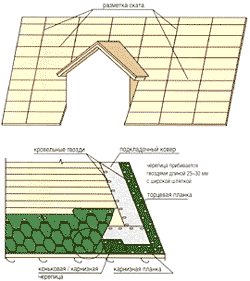
To ensure that the color of the roof is uniform during installation, tiles from several packages are used simultaneously. Bituminous shingles are laid in rows, from the edge of the roof up to the ridge. Work begins from the bottom of the slope from the center of the cornice in the direction of the gables.
The initial row is installed so as to ensure a distance of 2.0-3.0 cm between the lower edge of the tile petals and the beginning of the ridge/eaves tiles. The outermost tiles, from which the installation of the second row begins, is cut so that the roof pattern is formed and the mechanical fasteners of the previous one are overlapped row. Cut off the tiles along the edge gable cornice and treated with bitumen glue to a width of ten centimeters.
Fastening tiles
The installation of flexible tiles begins by removing the protective film from the shingles, then each tile is secured to the base using nails, usually 4-5 pieces. The next layer breaks through the previous one too.
Subsequently, under the influence solar heat the tiles will stick together and stick to the sheathing.
Making connections
Where the roof slope meets the wall, a triangular-shaped lath is nailed and soft tiles are placed on it. A strip of valley carpet is placed on top and glued with bitumen mastic. The approach of the strip onto the wall should be at least 30.0 cm, and in areas with heavy snowfall the approach should be increased. The junction is covered with a metal apron on top and treated with bitumen mastic.
Sealing the outlets of chimney pipes is carried out in a similar way, see the figure below.

When the cross-section of a brick pipe is more than 0.5x0.5 m and its location is across the slope, it is advisable to install a groove to avoid the accumulation of snow behind the pipe.
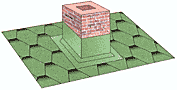

To pass antennas, communication pipes through the roof and seal roof passages, special passage elements for bitumen shingles are used, which are secured with nails.
The rows of soft tiles laid on the so-called penetration are cut and then glued to the flange with bitumen mastic. Then the required roof outlet is mounted on the passage element.

Ridge tiles are used for this. It is divided into three parts according to the perforation on it, laid with an overlap of five cm. The ridge tile is located with the short side along the line of the slope.

The installation of soft tiles is carried out in warm, dry times.
Any roofing material needs high-quality installation regardless of its cost and characteristics. Bituminous shingles are one of the most budget-friendly proposals, however, they can also provide reliable protection of the house from moisture if the installation technology is followed. In this article we will tell you everything you need to know to install bitumen shingles yourself.
Asphalt shingles are one of the most popular roofing materials, mainly due to their low cost and good protective characteristics. It is appreciated not only by professional builders, but also by self-taught people, since installation can be easily done on your own, even without special equipment. Bituminous shingles, also known as shingles, in contrast to small-wave ondulin, are characterized by greater aesthetics and versatility. However, these materials still have much in common in terms of manufacturing technology and composition. The tiles are unpretentious during installation and operation. Over time, it tends to “bloom,” but this only gives it a more noble appearance and does not in any way affect its protective abilities. The material is highly flexible and ductile. But even though installing bitumen shingles does not require special equipment or professional skills, you still need to know the specifics of the process. So, it can be used as a roofing material only when the roof has a slope of at least 12°. On a flatter slope, water will inevitably stagnate at the joints of the material, gradually destroying the coating and seeping inside the roofing pie. Installation is also affected by the weather. It’s clear that it makes no sense to build a roof when it’s raining outside. The performance characteristics of asphalt shingles respond to temperature changes. It can only be laid if the air temperature is from +5C. When it's cold outside, asphalt shingles lose their flexibility and elasticity, so the installation result will be of poor quality. If you still urgently need to make a bitumen roof in the cold season, keep the tiles in a warm room for several hours, and then install them on the roof as quickly as possible. The use of a hot air burner is also acceptable.
Material characteristicsSoft bitumen shingles are a durable and inexpensive roofing covering, characterized by good protective performance and aesthetics. Due to its light weight, it does not create a strong load on the floors and rafter beams, therefore it helps to save on construction (the rafter system can be made from beams of a smaller cross-section). Installation takes a minimum of time and effort, and any home craftsman can handle it. Asphalt shingles are essentially modified colored roofing felt that have been given a specific shape that resembles regular shingles. The thickness of the sheet of bitumen shingles can vary from 3 to 5 mm, the service life reaches 30-40 years. The structure determines the quality of the material. Most shingles are made up of 5 layers and may or may not have an adhesive coating.
Characteristics of bitumen shingles:
In addition to the main advantages that bitumen shingles have, they are distinguished by one more thing - a roof covered with them can be modified without much difficulty, since dismantling shingles is even faster and easier than installing them. For example, if you want to make a roof window, you will only need to remove a few “tiles” rather than removing the entire covering. Installation accessoriesTo lay a soft roof, bitumen shingles alone are not enough; you need to use various components. Thus, it is very important to use aerators to fully ventilate the internal space of the roofing pie. Without them, condensation will form on the thermal insulation layer, which will negate all the properties of the insulation. Aerators are placed in the roof slope or on the ridge. You can find two types of aerators in stores: for roofs with gentle slopes and for use in regions with heavy rainfall.
In addition to aerators, you will need valley and ridge elements. They have a structure similar to tiles, but without a decorative frame. They are fixed to areas of the roof that are most susceptible to damage, for example, on ridges, valleys, overhangs and around chimney pipes. To protect the overhangs, special PVC profiles are also used, fixing them on the eaves under the tiles. They do not allow water from the gutters to penetrate inside and play the role of a tin finish. If the house is located in a mountainous area or a region with heavy snowfalls, snow retainers should be used. Laying bitumen shinglesIn order for the installation of shingles to be successful, they must be properly transported and stored. To do this, choose a cool and shaded place. Do not lay shingles on open ground - be sure to place film or wood underneath them. Position the shingles front side up and do not stack pallets on top of each other. Deliver material to the roof in small batches.
Preparing the baseBefore laying bituminous tiles, it is necessary to prepare the surface - to create a solid or lattice base. In most cases, the crate is made of wooden slats or planed pine boards 20-25 mm thick. For a solid base, choose moisture-resistant plywood, chipboard or boards, fixing them with self-tapping screws or long nails. At the same time, keep in mind that small gaps of a few millimeters should be left between the elements in case of natural wood movements. You can do without gaps only if all the lumber has been subjected to technical drying.
The thickness of the sheathing boards is determined by the frequency of installation of the rafters. If it is 60 cm, then the thickness of the crate will be 20 mm, but if the rafters are located every 90 cm, the thickness of the crate should be increased to 23 mm, otherwise it will sag under the weight of the roofing cake. Ventilation of the under-roof spaceThe technology for laying bitumen shingles provides for ventilation of the under-roof space. This factor depends on the service life of all layers of the cake and rafter frame. Ventilation is provided by a ridge beam, which is mounted on a special ribbed profile. But it happens that it is not enough and it is necessary to install additional ventilation elements. They are ribbed plastic profiles, installed with a certain step. If the slope is 15-40°, the ventilation area is the area of the slopes / 300. If from 41° to 85° - the roof area / 600. For example, the total area is 50 m², the slope is 35°, the cross-section of the ventilation element is 258 cm². Then the ventilation area will be equal to 50\300 = 0.167 m² (1670 cm²), and the required number of elements will be 1670\258 = 5.
On skates, half as many ventilation elements should be installed as on slopes. In our case, you can put 3 pieces on the skate. Roof liningWhen working with the lining layer, you should take into account its operational purpose - protection from moisture in case of possible leaks. There are certain installation standards that state that if the roof has a slope of more than 18°, then the waterproofing lining should be laid parallel to the eaves and ends, since these are the most vulnerable areas. Waterproofing must be laid no further than 40 cm from the edge of the roof, but it would be best to extend it all the way to the façade. You should also protect the ridge beam from leaks by laying the lining so that it covers at least 25 cm on each side of the ridge.
For shoos with a small slope, things are somewhat different. So, if it is from 12° to 18°, then the waterproofing lining must be laid over the entire roof area, moving from bottom to top and overlapping the layers with each other. To fix the lining, galvanized nails with a wide hat are used. The installation step of the fasteners is usually 20 cm. Roof tiles: installationFinally, when everything preparatory work completed, you can begin laying bitumen shingles. Often, home-grown craftsmen make the same mistake - they first stack the material from one package, then open another, use it up, etc. This leads to the fact that the roof becomes “pockmarked” - tiles from different batches may differ in shade. It is clear that you cannot cover the entire roof with one package, so open several of them at once before work. As a result, the roof surface will turn out to be heterogeneous, but more or less uniform, which will give it uniqueness and visual volume.
Technology for creating a roof from bitumen shingles:  Tile jointsOften, when laying shingles, many craftsmen face difficulties in the form of various items on the roof. How to properly bypass them so as not to damage the integrity of the coating? If there is a chimney sticking out of the roof, how do you arrange its connection? In this place there will always be a gap through which moisture will penetrate under the coating.
To prevent this, you should know how to properly attach the material:
As you can see, there is nothing complicated in laying bitumen shingles. You just need to adhere to technology and observe personal safety rules when working at height. By the way, if after many years the tiles collapse or you simply want to change the color of the roof, you can safely install new shingles on top of the old covering. Bituminous shingles: photo
|
Soft roofing is a type of covering that has long been familiar to most people. Not so long ago, one of the most widely used materials for roofing various designs was an ordinary roofing material, which also belongs to this category of roofing. In fairness, it is worth noting that the old roofing material was not particularly durable and high performance, so it needed periodic repairs.
Today, thanks to new technologies that have appeared, soft roofing material has undergone significant modernization. It is produced in various options, including in the form of bitumen shingles. Such coatings already have long service life, combine high quality, excellent waterproofing characteristics and a very elegant appearance. Therefore, many do not even realize that a modern soft roof is still the same roofing material, only produced in improved variations.
The technology of laying a soft roof made of bituminous tiles is quite complicated and requires large quantity various materials, since the design of such a coating consists of several layers, which is why it deserves the name “roofing pie”. Therefore, if you decide to independently install a coating from this material, you must very carefully study all the recommendations that should be followed when performing the work.
Before deciding to choose a soft roof, you need to have an idea about this material and evaluate its advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages of soft roofs

There are several points that can be called disadvantages of this roofing material, but, to be honest, they are very arbitrary. So, such “cons” include:
- The installation of a “roofing cake” is quite complex, requiring strict adherence to all technological recommendations.
- Any soft roof is laid only on a solid solid base. And this, in turn, will additional work and, consequently, costs.
However, as you can see, there are much fewer negative aspects in arranging a soft roof, and therefore, more and more often, the owners of mansions are choosing it.
Various types of soft roofs
Soft roofing includes several types of materials that can easily be found on the Russian market - these are flexible bitumen shingles, rolled soft roofing various types, and euroslate (ondulin).
Rolled soft roofing

Roll roofing materials are divided according to several criteria. Thus, the following types of coatings are produced:
- Baseless and having a base for coating.
- Basis for roofing roll materials can serve - fiberglass, asbestos fiber, cardboard, polymers, or several materials can be used for it in combination.
- Roofing material can be equipped with various protective layers - fine-grained or coarse-grained mineral chips, dust or flake powder.
In addition, roll coatings can be divided according to the type of base and installation method:
- Self-adhesive coatings. Such a material has a layer of adhesive applied to the back of the web and protected by a special membrane, which is removed immediately before the installation of the coating.

- Glue-on sheets. These coatings are glued to mastic different ways which are called hot and cold. But in any case, the material during installation is heated to a certain temperature.
- Weldable coatings. This type of covering is fixed to the roof surface using gas burners. The burner flame melts the composition applied to the back side of the soft roofing material, after which the coating is rolled. This type of coating, properly laid on the prepared roof surface, makes it practically airtight and resistant to leaks. In addition, this type of material is considered the most durable of all roll options.
Membrane roll roofing

Membrane coating is a high-tech material that can be made on various bases: polyvinyl chloride (PVC), synthetic rubber (EPDM), thermoplastic polyolefin (TPO).

- The PVC membrane, reinforced with ether fiber and containing plasticizers, has high elasticity and resistance to temperature changes. In addition, the material does not fade in the sun, is fire resistant, is available in a range of colors, and is also easily and quickly mounted on the surface. However, this coating has its drawbacks - it is not resistant to organic solvents, to bitumen and oils. In addition, when heated, the PVC coating is capable of releasing substances toxic to humans into the air, since it is not environmentally friendly.
- EPDM membranes, made on the basis of rubber and reinforced with polyester meshes, have high elasticity and resistance to various solvents.
The negative qualities of this material can be called the fact that its installation is carried out with the help of glue, and joints over time, under the influence external factors, may diverge, and therefore the roof will begin to leak, as the coating will lose its tightness.
- TPO membranes made on the basis of thermoplastic polyolefin can be reinforced or produced without it. Polyester or fiberglass is used to reinforce this material. The material sheets are welded together using hot air, and a fairly strong and reliable seam is formed at the welding site. Therefore, the coating has a long service life, high strength and resistance to negative temperatures reaching -60 degrees.
The disadvantages of such a coating include its low elasticity and rather high cost compared to other membrane materials.
Briefly about the principles of laying membrane roofing material
There are four main installation methods membrane roofing- this is ballast fixation, mechanical fastening, gluing and hot air welding.
- Ballasting used if the roof has a slight slope not exceeding 15˚.
In this case, the canvas is laid on concrete base flat roof or on a layer of laid thermal insulation. Then the material is stretched, secured around the entire perimeter, and the joints of the sheets are connected using welding or special glue.

Then, ballast made of pebbles, gravel or crushed stone is placed on top of the membrane.
- Mechanical fastening is carried out if the supporting structure is not designed to support the weight of ballast.

The basis for installing the membrane in this way can be wood, concrete, profiled sheets, as well as any other material.

A layer is laid and secured onto the base insulation material. Most often, high-density mineral basalt wool, specially designed for this application, is used for this, on top of which a membrane is spread and fixed. To fix materials to the base, disk or telescopic fasteners are used, which are installed at the joints of sheets overlapped by 80÷100 mm.
- Membrane gluing is produced using high-quality adhesive mixtures characterized by good strength. The material is glued only around the perimeter of the canvas, at joints and in problem areas, for example, around chimneys, on ribs, valleys, etc.
- Membrane welding with hot air- this method more often It is generally used for fastening sheets of membranes.

The work is carried out using a special apparatus that compresses two overlapping sheets using a roller and hot air, the temperature of which reaches 600˚C. The welded joint can be from 20 to 100 mm wide, which ensures the reliability of the connection and guaranteed sealing.
Euroslate or Ondulin

Another option for roofing material, which can also be classified as a soft roof, is ondulin or euroslate. This is a lightweight and reliable wavy material made from a bitumen-fiber mixture with the addition of mineral and polymer additives. Roofing sheets are easy to install and usually have a very long service life. The material is produced in various shades of calm tones, from which you can always choose the one suitable for a specific facade design.
Installation of this material can be carried out not only on a solid base, but also on a lathing made of boards 150÷170 mm wide, fixed in increments of 200÷250 mm.
Ondulin is the only material from the soft roofing category that has a fairly rigid relief structure, and therefore can be attached to the sheathing.

Installation of ondulin, like any wavy roofing material, is carried out from the eaves. The upper rows are laid with an overlap on the lower ones by 250 ÷ 300 mm, and adjacent sheets located in the same row are mounted overlapping, on one wave. Ondulin is fastened with special screws with waterproofing gaskets and special covers. They are screwed into each wave crest along the cornice and ridge, and in the middle part of the slope - in increments of two to three waves.
Flexible bitumen shingles

Bituminous shingles can easily be considered one of the most popular types of soft roofing, as they are distinguished by their aesthetic appearance, a variety of shades and shapes, strength and durability.
The tiles are made on a fiberglass base, which is impregnated with high-quality bitumen, on top of which mineral chips of various colors are applied. The top mineral coating performs not only a decorative function, but also a protective one, as it prevents mechanical damage to the softer lower layers. Tiles are used to cover houses with pitched roofs of any size and configuration of any degree of complexity.
Since the most popular material in the soft roofing category is bituminous shingles, its installation will be discussed in more detail.
Installation of roofing with bitumen shingles
First, it’s worth understanding the roofing “pie” that needs to be mounted under the soft tile flooring. It is very important to do this work correctly, otherwise the roof will be deprived of reliability and will not last a long time, and it will be impossible to maintain a comfortable microclimate in the rooms under it.
Approximate sequence of work
In order to follow the sequence of installation of all elements, it is best to compile a list of all works in order:

- The first step is the installation of the rafter system.
- Next, a vapor barrier membrane is attached to the rafters from the attic side.
- On top of the vapor barrier, also from the side of the attic, a crate of timber is fixed to the rafters. It is needed for subsequent installation internal lining attic space, fixing the membrane and creating a rigid base for laying insulation.
- Next comes the laying between rafter legs insulation mats. Typically, mineral basalt wool is used for this.
- The insulation is covered with a waterproofing roofing membrane. It is fixed to the rafters.
- The membrane is pressed against the rafters using counter beams.
- Next comes the installation of sparse sheathing - the basis for laying a solid base.
- Sheets of moisture-resistant plywood or OSB are fixed on the crate.
- A solid plywood crate is covered with a lining carpet.
- Next, the laying of soft bituminous tiles is underway.
- Fastening the drainage system, covering the eaves overhang with mosquito netting, and then with lining or PVC soffits can be carried out at various stages of installation work - as will be more convenient for the craftsmen.
Calculations of the lathing system for a soft roof
Now knowing the approximate sequence of installation of the “roofing cake”, there is a need to consider them in more detail, since there are nuances that are important to take into account when performing these rather complex technological operations.
The first thing that needs to be determined is what parameters the elements of the rafter system and sheathing should have, and with what step they are installed.
Let's start with the rafters. The cross-section of the timber from which they are made depends on the steepness of the slope, possible external loads on the roof and on the installation step of the rafter legs. The dependence is expressed as follows.
External loads include the weight of the structure itself, with insulation, lathing and roofing material, the mass of possible snow deposits in winter time and exposure to winds. Both snow and wind loads strongly depend on the steepness of the slope, and with an increase in the angle of inclination, the significance of the snow load gradually decreases, but the wind load increases.
Total load expressed in kilograms per square meter, should be evenly distributed over the rafters. And this, in turn, depends on the step of their installation - the more often they are located, the less load falls on each linear meter of the rafter beam, and the smaller its cross section can be. If the value of the distributed load is known, then it is easy to determine the parameters of the required material from the table.
There is a rather complex physical and mathematical algorithm for calculating the distributed load on the rafter legs. But we will not bore the reader with an abundance of formulas and tables, but we will suggest using a convenient calculator. The initial data for the calculation will be:
— Region of construction;
— Steepness of the roof slope, degrees;
— Material roofing;
— Features of the location of the house on the ground and its height.
In the last paragraph of the calculator you will need to indicate the expected installation step of the rafters. By changing this value up or down, you can determine the optimal load distribution. And then, according to the table, knowing the length of the rafters, select the required section of the beam (log).
Attached to the calculator are two schematic maps that make it possible to determine the zones of the construction region based on the level of snow and wind load.
Calculator for calculating the distributed load on rafter legs
So, to begin with, we determine the zones using maps and diagrams:


Now we substitute the known values into the calculator and get the result



















